If you are constantly tired, your eyes are trembling and you have muscle spasms, there is probably a lack of magnesium in your body. A magnesium deficiency can cause serious illness because many processes in the body depend on it. That is why you must be alert and identify a deficiency in time.
Sign And Symptoms Of Magnesium Deficiency
8. Sugar Food Cravings

A burning desire to eat something sweet shows that there is a lack of certain minerals in the body, particularly magnesium.
Magnesium loss in women is generally related to menstruation and athletes with intense training when the body expends magnesium on muscle work.
7. Muscle Soreness And Cramping
Muscle cramps and soreness can be very painful. If you have them regularly, it may be a sign of low magnesium levels. Magnesium and vitamins D, E, and B can prevent muscle cramps.
Therefore, visit your doctor to check the levels of these vitamins and make sure you get the recommended daily dose of them.
Also, you can try to alleviate your suffering by massaging the affected muscles in a circular motion.
6. Insomnia
Magnesium deficiency can cause insomnia. Magnesium is vital for a function called “brain relaxation.” This ability of the brain helps us relax and fall asleep calmly.
As we mentioned earlier, low magnesium levels can lead to muscle cramps. This causes restless feet syndrome, a condition that makes your legs tremble at night. As a result, the quality of your sleep declines.
5. Bone Disease
Magnesium deficiency can also increase the risk of developing bone problems. This can lead to an increased risk of fracture.
The point is that magnesium deficiency can lower the level of calcium in the blood, and calcium is essential for keeping bones healthy.
4. Acid Reflux

If you have a magnesium deficiency, food, and stomach acid return to the esophagus. This leads to a burning sensation, called acid reflux or heartburn.
3. Stress And Apathy

Magnesium is an essential element to build a strong nervous system. This element is responsible for relaxation.
With a lack of magnesium in the body, a person feels anxiety and stress without cause. Therefore, the risk of depression increases dramatically.
2. Constipation
There are many reasons why you can get constipated, from stress to low fiber intake. Magnesium has a relaxing effect on many parts of the body, including the digestive tract.
Due to the lack of this mineral, the intestinal functions do not work properly, leading to constipation.
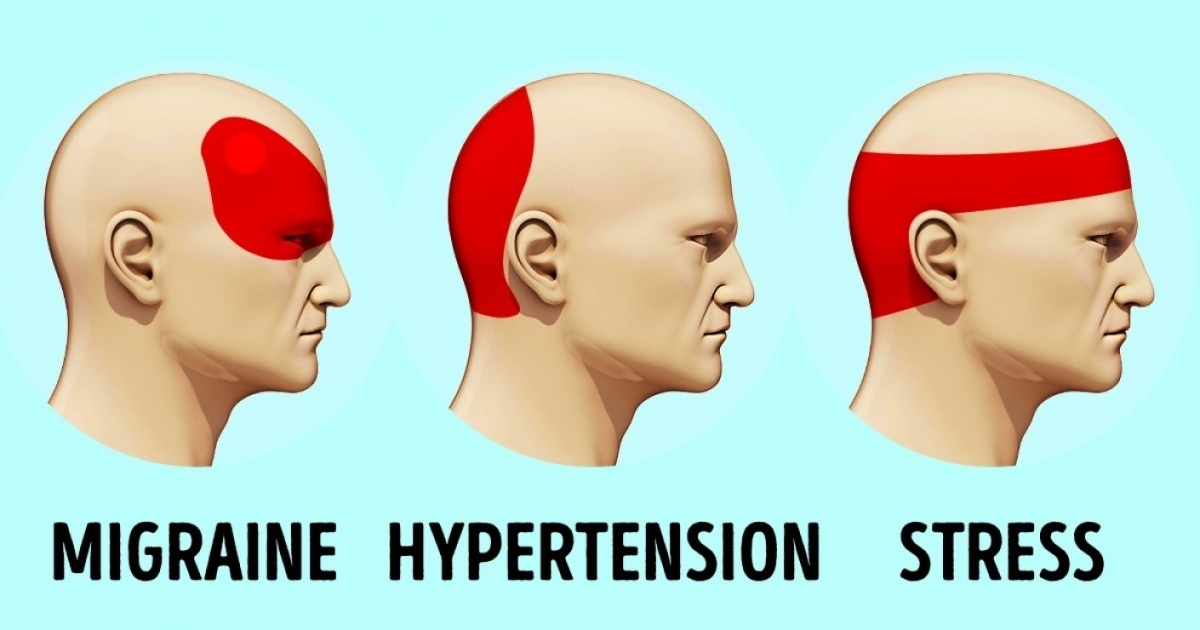
1. Severe Headache
If you don’t have all of these areas (vitamins A, B, C, and D), this can lead to a very severe headache. Migraines generally affect only one side of the head.
Magnesium deficiency can cause frequent migraines and headaches. With a deficiency of this mineral, the blood vessels in the brain rapidly narrow and expand, which is the cause of a migraine.
Sufficient magnesium in the body reduces the risk of changes in the blood vessels and eliminates headaches.
Best Food For Magnesium Deficiency

A balanced diet can provide the body’s daily magnesium requirement. Many people do not get enough magnesium because they lead a healthy lifestyle.
Here is a list of foods that can increase your magnesium level:
- Nuts and seeds
- Cereals
- Beans
- Fresh and dried fruits
- Vegetables
- Fish
Have you noticed any signs of magnesium deficiency in your body? What helped you deal with these symptoms? Share your experience with us in the comments!