Gluten sensitivity, also known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), affects millions worldwide. Unlike celiac disease—an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten—gluten sensitivity doesn’t damage the intestines but can still cause debilitating symptoms. Research suggests that 6% of the global population may suffer from NCGS, yet many remain undiagnosed. Recognizing the signs is crucial for improving quality of life and preventing long-term complications.
In this article, we’ll explore the seven most common symptoms of gluten sensitivity, backed by science and expert insights. Whether you’re experiencing unexplained weight changes or chronic fatigue, understanding these signs could be the first step toward reclaiming your health.
Symptoms Of Gluten Sensitivity
7. Gastrointestinal Issues: The Hallmark of Gluten Sensitivity

Digestive problems are the most frequently reported symptoms of gluten sensitivity. When gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye—irritates the gut lining, it can trigger inflammation and disrupt digestion. Common gastrointestinal signs include:
- Bloating and gas after meals containing gluten
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal pain resembling irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
A 2020 study highlighted that over 50% of gluten-sensitive individuals experience IBS-like symptoms. Unlike celiac disease, NCGS doesn’t show up on standard blood tests, making symptom tracking essential. If eliminating gluten alleviates these issues, it may indicate sensitivity.
Pro Tip: Keep a food diary to identify patterns between gluten consumption and digestive distress.
6. Unexplained Weight Fluctuations: A Hidden Consequence
Sudden weight loss or gain without changes in diet or exercise can signal gluten sensitivity. Here’s why:
- Weight Loss: Malabsorption due to gut inflammation can prevent nutrient uptake.
- Weight Gain: Chronic inflammation may spike cortisol levels, promoting fat storage.
A study in Nutrition & Diabetes linked gluten consumption to insulin resistance in sensitive individuals, further complicating weight management. If your weight fluctuates unpredictably, consider discussing gluten intolerance with your healthcare provider.
5. Hormonal Imbalances: The Gluten-Endocrine Connection
Gluten sensitivity can wreak havoc on hormonal health, particularly in women. Symptoms include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Severe PMS or mood swings
- Fertility issues or recurrent miscarriages
Research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism suggests gluten may interfere with estrogen metabolism, exacerbating conditions like PCOS. Balancing hormones often requires a gluten-free diet paired with medical guidance.
4. Central Nervous System Symptoms: Brain Fog, Fatigue, and More
Gluten’s impact isn’t limited to the gut—it can also affect the brain. Common neurological symptoms include:
- Chronic headaches or migraines
- Brain fog (difficulty concentrating)
- Anxiety or depression
A 2021 review found that gluten-sensitive individuals are three times more likely to experience migraines. The inflammatory response triggered by gluten may damage neural pathways, leading to these cognitive and mood-related issues.
3. Skin and Nail Problems: External Clues of Internal Inflammation
Skin conditions often mirror internal inflammation caused by gluten sensitivity:
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH): An itchy, blistering rash affecting 15-25% of gluten-sensitive individuals (American Academy of Dermatology).
- Acne or Eczema: Linked to gut inflammation and leaky gut syndrome.
- Brittle Nails: Nutrient deficiencies from malabsorption weaken nails.
Adopting a gluten-free diet often improves these conditions within weeks.
2. ADHD: The Overlooked Link to Gluten

Emerging research suggests a connection between gluten sensitivity and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Symptoms like impulsivity and poor focus may improve on a gluten-free diet. A 2019 study found that 30% of ADHD patients experienced symptom relief after eliminating gluten, likely due to reduced neuroinflammation.
1. Dental Health Issues: Enamel Defects and Cavities
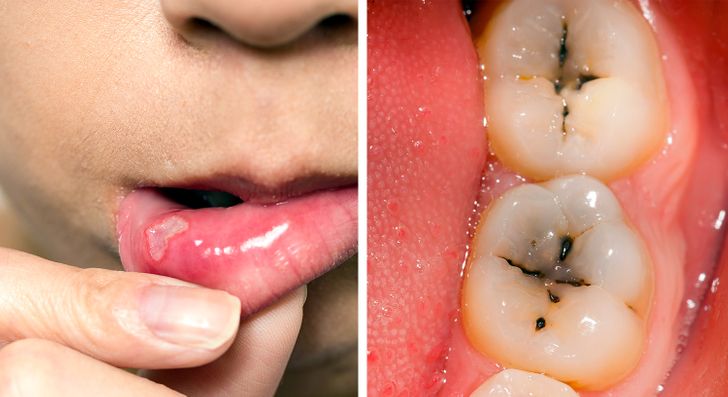
Frequent cavities or enamel defects may indicate gluten sensitivity. Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D—critical for dental health—can weaken teeth. Additionally, research in BMC Gastroenterology notes that gluten-sensitive individuals are prone to mouth ulcers and cracked teeth.
Next Steps: Managing Gluten Sensitivity
If you identify with these symptoms:
- Consult a Doctor: Rule out celiac disease with blood tests or a biopsy.
- Try an Elimination Diet: Remove gluten for 4-6 weeks, then reintroduce it to observe reactions.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize naturally gluten-free foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
For personalized advice, consider working with a registered dietitian specializing in gluten-related disorders.