In our modern world, we often pride ourselves on following hygienic practices and routines, believing they keep us safe and healthy. However, some of these seemingly innocent habits can inadvertently pave the way for health issues and disease transmission. From reusing food bags to defrosting food at room temperature, everyday actions may carry hidden risks that undermine our well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll examine nine common hygienic habits that secretly ruin our health, backed by expert insights and reputable sources. By understanding these pitfalls, you can adjust your routines for a safer, healthier lifestyle while maximizing disease prevention and overall wellness.
Bad Personal Hygiene Habits
Cleaning Winter Clothes in Spring: The Hidden Dangers of Out-of-Season Washing

When winter turns into spring, many of us rush to clean our winter clothes in an effort to get rid of accumulated odors and grime. While this may seem like an innocuous seasonal chore, improper cleaning practices can inadvertently lead to the spread of allergens and bacteria.
Seasonal Allergen Buildup:
Winter clothing can harbor dust mites, mold, and other allergens that thrive in the cold. As the weather warms up, these contaminants may be released into the air during cleaning, exacerbating respiratory issues and allergies. For those prone to seasonal allergies, this process can worsen symptoms and trigger asthma attacks.
Optimal Cleaning Practices:
Experts recommend washing winter garments separately using a hypoallergenic detergent and running them on a hot cycle to effectively eliminate allergens. Additionally, consider using a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter in your dryer to capture airborne particles. For further reading on allergens and proper cleaning techniques, check out Mayo Clinic’s advice on managing allergies.
Defrosting Food at Room Temperature: A Recipe for Bacterial Growth

One common kitchen shortcut is defrosting frozen food by leaving it out at room temperature. While this method may save time, it poses significant risks for food safety.
Bacterial Multiplication Danger:
When food is left out to thaw, its surface temperature can enter the “danger zone” (40°F to 140°F), where bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli multiply rapidly. This increases the risk of foodborne illnesses and contamination. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) warns against defrosting meat, poultry, and other perishables at room temperature due to these risks.
Safer Alternatives:
To prevent harmful bacterial growth, defrost food in the refrigerator or use the microwave’s defrost setting. These methods keep your food at a safe temperature, minimizing the chance of contamination. Learn more about safe food handling practices from the USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service.
Sharing Food With Friends: When Social Habits Risk Your Health
Sharing food is a time-honored social practice, often seen as a sign of generosity and camaraderie. However, if not done with proper hygiene in mind, it can become a conduit for germ transmission.
Cross-Contamination Concerns:
When you share food, you might unknowingly transfer bacteria and viruses from your hands or utensils to the shared dish. This risk increases during communal meals, especially if individuals are not following strict hygiene protocols. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advises that proper handwashing and the use of clean utensils are essential in preventing the spread of infectious diseases during shared meals.
Smart Sharing Practices:
To enjoy the social benefits of sharing food without compromising health, consider using serving utensils and small, individual portions. Encourage all participants to wash their hands before eating. For additional insights on preventing foodborne illnesses in social settings, visit the CDC’s guidelines on food safety.
Washing Hands with Hot Water: When Comfort May Compromise Skin Health

Handwashing is a cornerstone of personal hygiene, yet the temperature of the water used can have unintended consequences. While hot water may feel soothing, it is not always the best choice for effective hand hygiene.
Impact on Skin Barrier:
Hot water can strip away natural oils from your skin, leading to dryness, irritation, and even cracks in the skin barrier. This damage can make your hands more susceptible to infections and allergic reactions. Dermatologists recommend using lukewarm water, which is effective in removing germs without causing undue dryness.
Optimizing Handwashing Technique:
Incorporate a gentle soap and ensure you’re scrubbing for at least 20 seconds, as advised by the CDC’s handwashing recommendations. This approach not only cleans your hands thoroughly but also preserves the natural moisture barrier essential for healthy skin.
Using a Hand Dryer: The Unexpected Health Risks of Airborne Germs
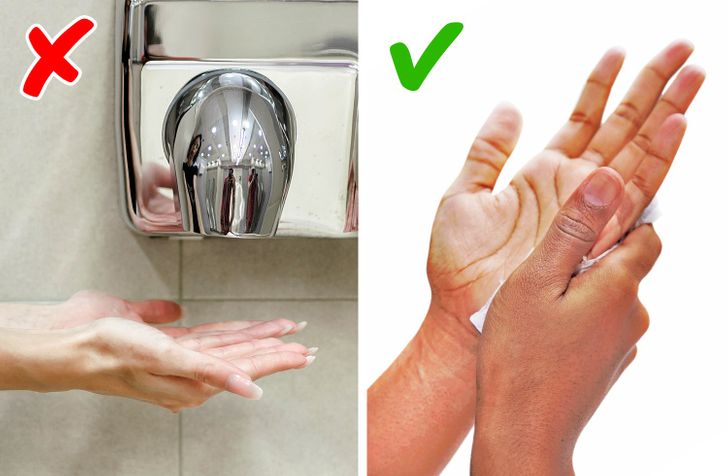
Hand dryers are a common sight in public restrooms, but recent studies suggest that their use might spread germs rather than eliminate them.
Aerosolization of Bacteria:
Many modern hand dryers can aerosolize bacteria, dispersing microscopic droplets across the surrounding area. This process can increase the risk of transmitting infections, especially in high-traffic public spaces. Research published in journals such as the Journal of Applied Microbiology has indicated that hand dryers may not be as hygienic as paper towels.
Safer Alternatives:
For improved hygiene, consider using paper towels or personal hand sanitizers in public restrooms. When paper towels are used properly, they can significantly reduce the risk of airborne bacteria. For more information on the pros and cons of hand dryers versus paper towels, read the analysis on Healthline.
Reusing Food Bags: How One-Time Use Can Save You from Foodborne Illness

Many of us reuse food bags to save money and reduce waste. However, reusing these bags without proper sanitation can lead to cross-contamination and bacterial buildup.
Bacterial Contamination Risks:
Food bags, especially those that have contained raw produce or meat, can harbor dangerous bacteria if not washed thoroughly between uses. This residue can transfer to other foods, increasing the risk of food poisoning. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) emphasizes proper cleaning practices for reusable food containers to minimize these hazards.
Best Practices for Reuse:
If you choose to reuse food bags, ensure they are washed with hot water and a disinfectant solution after each use. This simple step can help mitigate the risk of bacterial growth and ensure safe food storage. Visit the FDA’s guidelines on food packaging for additional safety tips.
Cutting Meat and Vegetables on the Same Board: Avoiding Cross-Contamination in the Kitchen
Using a single cutting board for both meat and vegetables is a common kitchen shortcut, but it can lead to dangerous cross-contamination if proper care isn’t taken.
Pathogen Transfer:
Raw meat can contain harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli. When vegetables are cut on the same board, these pathogens can transfer onto the produce, potentially leading to foodborne illnesses. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) strongly recommends using separate cutting boards for raw meats and fresh produce to prevent such risks.
Implementing Safe Kitchen Practices:
Invest in color-coded cutting boards to designate specific boards for meats, vegetables, and other food items. Additionally, thoroughly sanitize cutting boards with hot, soapy water or a diluted bleach solution after each use. For further details on preventing food contamination, check out the CDC’s food safety recommendations.
Using an Office Coffee Machine: Hidden Germs Lurking in Your Daily Brew

Office coffee machines are a staple in many workplaces, but they can also be hotspots for germs and bacteria. Frequent use coupled with inadequate cleaning can turn these machines into reservoirs of contamination.
Bacteria Buildup in High-Traffic Areas:
Shared coffee machines accumulate bacteria from the frequent handling of cups, taps, and internal components. Over time, this buildup can lead to unpleasant odors and even affect the taste of your coffee. Studies have shown that the warm, moist environment inside coffee machines is ideal for bacterial growth. For insights on workplace hygiene and equipment maintenance, see Verywell Health’s guide on office wellness.
Optimizing Office Coffee Hygiene:
Encourage regular maintenance and deep cleaning of office coffee machines to minimize health risks. In addition, consider using personal mugs and disposable liners where appropriate to reduce contact with shared surfaces.
Keeping Your Phone in Your Purse: The Surprising Risks of Mobile Contamination

Smartphones are an integral part of our daily lives, yet their hygiene is often overlooked. When you keep your phone in your purse, it can become a breeding ground for germs, transferring bacteria every time you handle it.
Mobile Germ Hotspots:
Research has revealed that mobile phones can harbor more bacteria than a toilet seat. When stored in a purse or bag, phones come into contact with various surfaces and contaminants, increasing the risk of cross-contamination. The CDC advises regular cleaning of mobile devices to reduce the transmission of pathogens.
Simple Steps for Safer Mobile Hygiene:
Consider wiping your phone daily with alcohol-based wipes or a microfiber cloth to remove harmful bacteria. Additionally, keep your phone in a separate compartment rather than in your purse, especially if you frequently handle food or other high-contact items.
Conclusion: Rethinking Everyday Habits for a Healthier Future
While many of our daily habits are rooted in tradition and convenience, it’s crucial to reexamine them in light of modern health challenges. From cleaning winter clothes in spring to reusing food bags and even the way we interact with shared office coffee machines, these practices—if not managed properly—can have a profound impact on our overall health.
By understanding the hidden risks associated with these innocent hygienic habits, you can take proactive steps to optimize your routines, reduce exposure to harmful bacteria, and protect your well-being. Simple adjustments like using separate cutting boards, opting for safe food defrosting methods, and maintaining proper mobile hygiene can go a long way in preventing infections and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Implementing these changes not only minimizes health risks but also supports a robust, disease-preventive lifestyle. As you incorporate these tips into your daily routines, remember that small improvements can lead to significant benefits over time. The combination of expert recommendations from sources like the CDC, Mayo Clinic, and FDA reinforces that being mindful of even the most routine habits is key to long-term health.
Embrace a proactive approach to hygiene and wellness—by rethinking everyday actions, you can safeguard your health and enjoy a cleaner, safer environment. Whether you’re at home, at work, or on the go, making informed choices about your hygienic practices is an investment in your future.









