Pain is a complex and multifaceted signal from our body that something might be wrong. Understanding what really causes you pain is crucial not only for finding effective treatment but also for preventing further complications. In this comprehensive guide, we dive into the origins of pain in various parts of the body—from the heart and kidneys to the intestines, lungs, appendix, stomach, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas. With insights supported by medical research and expert advice, this article aims to help you decode your symptoms and take proactive steps toward effective pain management. Whether you’re dealing with chronic discomfort or occasional pain, understanding the root cause is the first step in your journey to better health.
For more detailed medical insights, trusted resources such as Mayo Clinic, WebMD, and Healthline provide excellent additional information.
What Different Types of Pain Are There
Understanding Heart Pain: Common Causes and When to Seek Medical Help
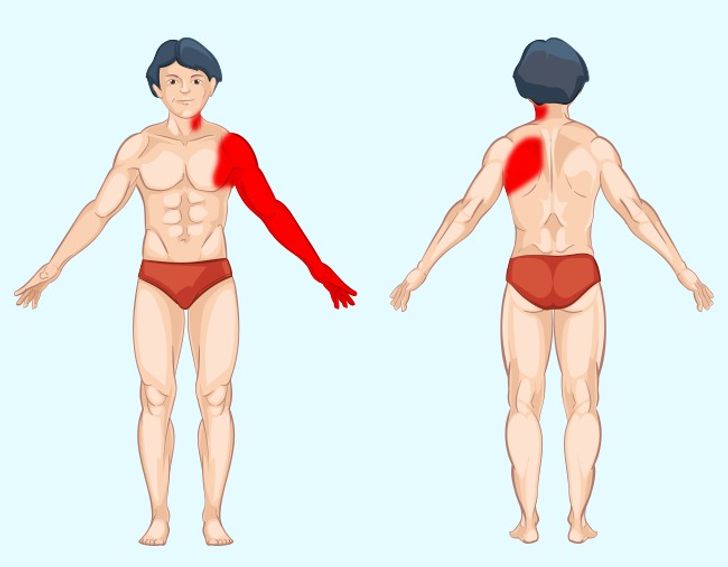
Heart pain, often referred to as angina, can be alarming and is a critical signal that warrants immediate attention.
What Causes Heart Pain?
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): A leading cause of heart pain is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack): Sudden and severe heart pain may indicate a heart attack, which occurs when a blockage prevents blood flow entirely.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart, can also cause sharp, stabbing pain.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of heart pain may include pressure or tightness in the chest, pain radiating to the arm or jaw, shortness of breath, and sweating. If you experience these symptoms, it’s critical to seek medical attention immediately.
For more detailed information on heart pain and its causes, visit the Mayo Clinic’s heart health page.
Kidney Pain: Identifying the Causes and Understanding Warning Signs
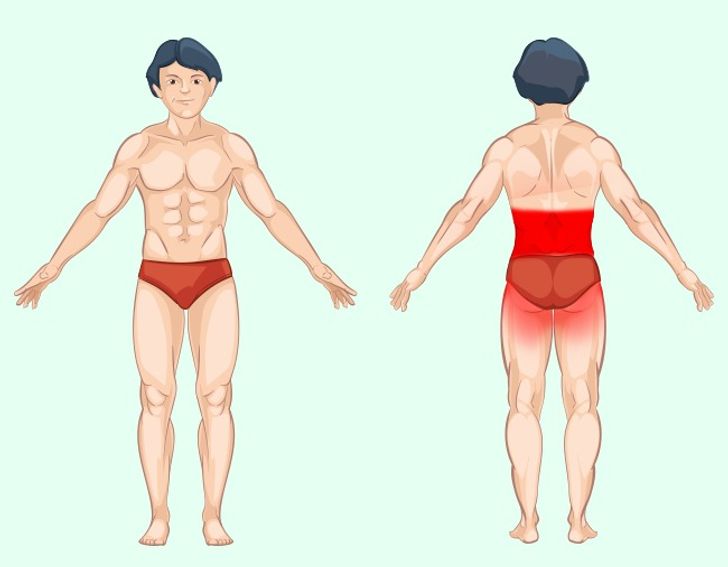
Kidney pain, often felt in the back or side, is usually a signal that something is affecting these vital organs.
Common Causes of Kidney Pain
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits formed from minerals and salts can block the urinary tract, causing severe pain.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections in the kidneys can result in discomfort and tenderness.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease: This genetic disorder causes fluid-filled cysts to develop in the kidneys, leading to pain and impaired function.
How to Recognize Kidney Pain
Kidney pain is typically characterized by a deep, dull ache in the flank or lower back, often accompanied by fever, nausea, or changes in urine output. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications.
For further insights into kidney pain and related conditions, refer to Healthline’s kidney health section.
Small Intestine Pain: Uncovering the Underlying Causes
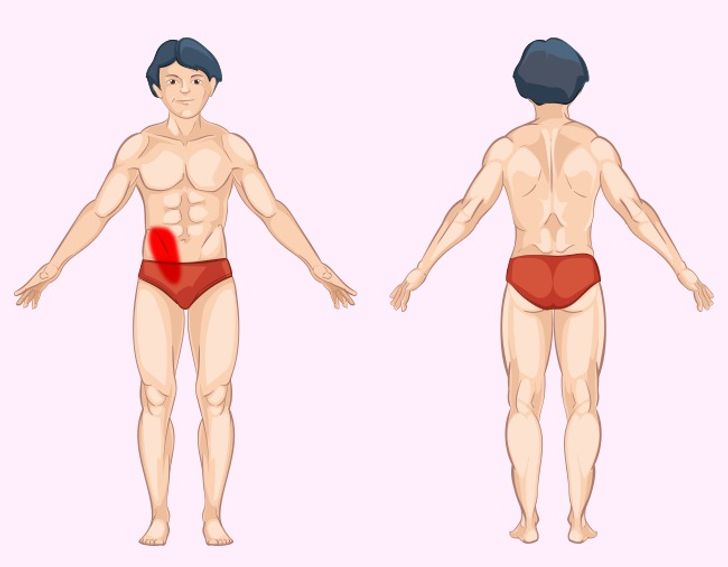
Pain in the small intestine can be challenging to diagnose due to its deep location and complex function in digestion.
Potential Causes of Small Intestine Pain
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions such as Crohn’s disease can cause inflammation and pain in the small intestine.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can lead to pain, cramps, and diarrhea.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional disorder causing pain and discomfort in the small intestine, often triggered by stress or certain foods.
Recognizing Symptoms
Small intestine pain may be accompanied by bloating, cramps, diarrhea, or constipation. A proper medical evaluation is necessary to differentiate between these conditions and establish an effective treatment plan.
For more comprehensive information on small intestine pain and its management, explore resources on WebMD’s digestive health section.
Large Intestine Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
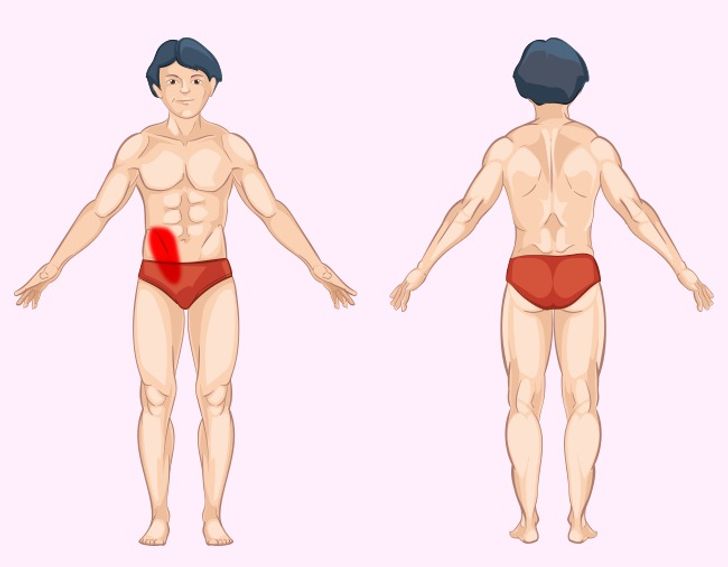
The large intestine plays a key role in water absorption and waste elimination, and pain in this area can signal a range of digestive issues.
Common Causes of Large Intestine Pain
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Characterized by chronic pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection of small pouches that can form in the colon wall, causing severe abdominal pain.
- Colon Cancer: Although less common, persistent pain in the large intestine can be an early sign of colorectal cancer.
Recognizing and Managing Large Intestine Pain
Symptoms often include cramping, persistent abdominal discomfort, and changes in bowel habits. Early detection through screenings like colonoscopies is crucial for effective treatment.
For additional insights on large intestine pain, refer to Mayo Clinic’s digestive health resources.
Lung Pain: Exploring Respiratory Causes and Warning Signs
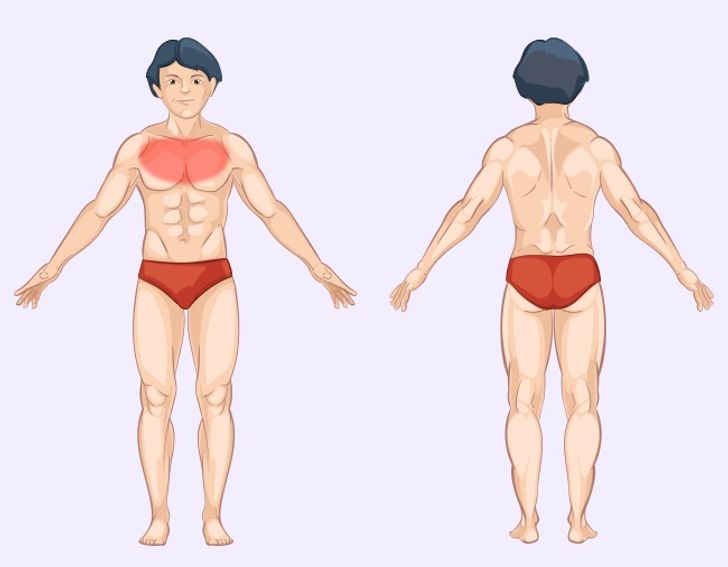
Lung pain, or pleuritic pain, can be alarming as it often signals an issue within the respiratory system.
Common Causes of Lung Pain
- Pneumonia: An infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, causing sharp chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs, usually caused by blood clots, which can result in sudden, severe pain.
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the tissues that line the lungs and chest cavity, often leading to sharp, stabbing pain.
Recognizing Respiratory Pain
Lung pain can manifest as a sharp or burning sensation that worsens with deep breaths or coughing. Prompt medical attention is critical if lung pain is accompanied by difficulty breathing, fever, or rapid heartbeat.
For more detailed information on respiratory pain and lung conditions, visit WebMD’s lung health section.
Appendix Pain: When to Worry About Abdominal Discomfort
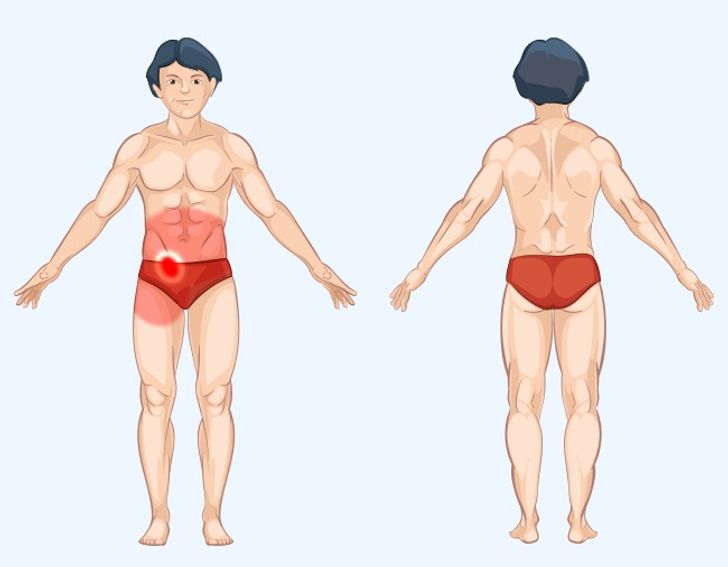
Appendix pain is most commonly associated with appendicitis, a condition that requires urgent medical intervention.
What Causes Appendix Pain?
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix is the primary cause of appendix pain. It typically starts as a dull pain around the navel and then shifts to the lower right abdomen.
- Other Conditions: Although less common, conditions like gastrointestinal infections or even certain cancers can mimic the symptoms of appendicitis.
Warning Signs and When to Seek Help
Symptoms of appendicitis include sharp pain in the lower right abdomen, fever, nausea, and loss of appetite. If these symptoms occur, seek medical help immediately, as prompt treatment is critical to prevent rupture and further complications.
For more on the signs of appendicitis and when to seek emergency care, check out the Mayo Clinic’s appendicitis guide.
Stomach Pain: Common Causes and Effective Management
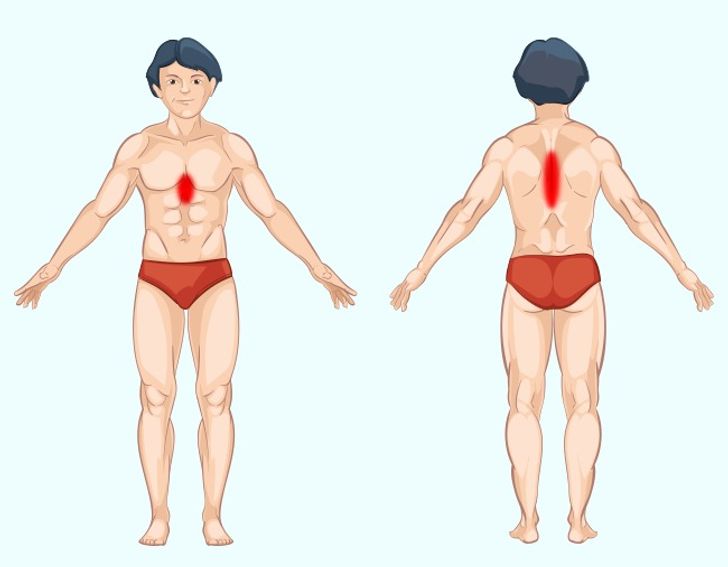
Stomach pain is one of the most frequent complaints and can result from a variety of conditions, ranging from mild indigestion to severe ulcers.
Causes of Stomach Pain
- Gastritis and Ulcers: Inflammation of the stomach lining and peptic ulcers can cause burning or sharp pain.
- Indigestion: Overeating, spicy foods, or stress can lead to indigestion, resulting in discomfort and bloating.
- Food Intolerances: Allergies or sensitivities to certain foods, such as lactose or gluten, may cause significant abdominal pain.
Managing Stomach Pain
Effective management of stomach pain involves dietary adjustments, stress reduction, and sometimes medications such as antacids or proton pump inhibitors. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods is also essential for long-term relief.
For further reading on stomach pain and digestive health, visit Healthline’s gastrointestinal section.
Gallbladder and Liver Pain: Understanding Symptoms and Underlying Causes
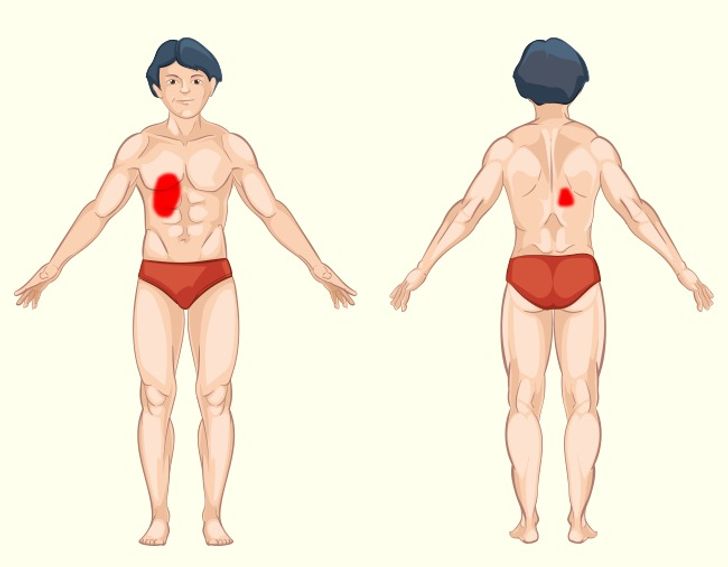
Pain originating from the gallbladder or liver can be challenging to pinpoint but is often a sign of serious underlying conditions.
Causes of Gallbladder Pain
- Gallstones: Hard deposits that form in the gallbladder can block bile ducts, causing sharp pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones, leads to severe pain and requires prompt medical attention.
Causes of Liver Pain
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver due to viral infections, alcohol abuse, or other toxins can cause discomfort in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
- Liver Cirrhosis: Long-term liver damage from various causes can lead to scarring and pain, along with other serious complications.
Recognizing the Signs
Symptoms may include dull, aching pain in the upper right abdomen, jaundice (yellowing of the skin), and unexplained weight loss. Early detection through imaging tests and blood work is essential for managing these conditions effectively.
For more detailed information on gallbladder and liver pain, see the resources provided by the American Liver Foundation.
Pancreas Pain: Recognizing Pancreatitis and Other Contributing Factors
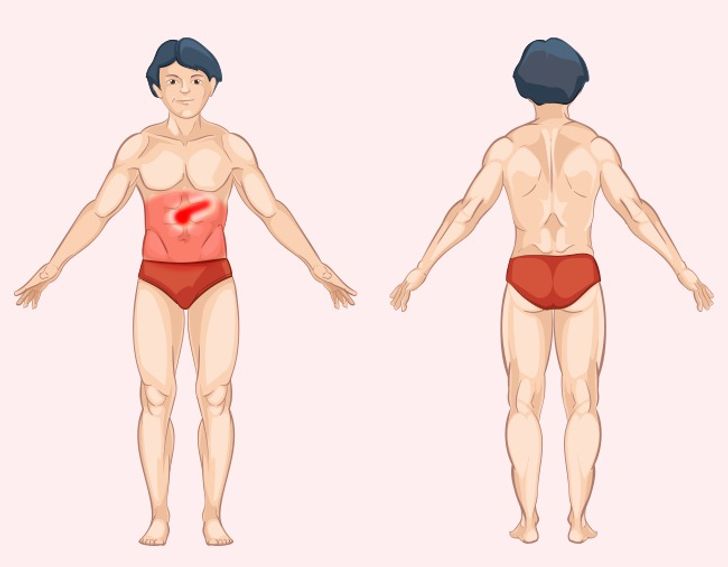
The pancreas plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. When it becomes inflamed, the resulting pain can be severe and debilitating.
Common Causes of Pancreas Pain
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, often triggered by gallstones or chronic alcohol use, is the primary cause of pancreatic pain.
- Pancreatic Cancer: Although less common, pancreatic tumors can also cause pain, usually accompanied by other systemic symptoms.
Symptoms and When to Seek Help
Pancreatic pain is often described as a deep, constant pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back. It is usually accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fever. Because pancreatitis can rapidly become a medical emergency, immediate evaluation is crucial if these symptoms are present.
For further insights into pancreas health and pain management, refer to Mayo Clinic’s pancreatitis information.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Pain and Seeking Professional Guidance
Understanding what really causes your pain is the first step toward effective treatment and improved quality of life. Whether it’s pain from the heart, kidneys, intestines, lungs, appendix, stomach, gallbladder, liver, or pancreas, recognizing the symptoms and potential underlying causes empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
Early detection, proper diagnosis, and a comprehensive treatment plan can dramatically reduce the impact of pain on your life. While this guide provides an overview of common pain causes, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for a personalized evaluation and treatment plan. Remember, your body’s signals are valuable—pay attention to them and don’t hesitate to seek expert advice.
For more detailed information on pain management and healthy living, explore trusted sources like WebMD, Healthline, and the Mayo Clinic. Taking proactive steps today can lead to a future with less pain and a better quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment of any health conditions.
Preview photo credit depositphotos