Our genetic makeup is a mosaic of influences from both our parents, but have you ever wondered if certain traits are uniquely inherited from your father? In this blog post, we dive into the intriguing world of paternal genetics and explore 5 traits that you can only inherit from your father. From determining your gender to shaping your physical features, these traits offer a fascinating glimpse into how paternal genes contribute to who you are today. We’ll break down each trait—height, crooked teeth, gender, dimples, and fingerprints—and discuss the scientific insights behind them. With expert commentary and credible external references, this comprehensive guide is optimized for SEO and designed to help you understand the significant role of your father’s genetics in your development.
Understanding the mechanics of genetic inheritance can be complex, but the influence of your father’s DNA is undeniable in many aspects of your physical and even behavioral characteristics. Let’s explore the top five traits that you might only inherit from your father.
Inherited Height: How Your Father’s Genes Impact Your Stature

Height is one of the most noticeable physical traits influenced by genetics, and numerous studies have shown that a significant portion of your height is determined by the genes you inherit from your father. While both parents contribute to your overall stature, paternal genetics play a crucial role in the expression of height.
The Genetics of Height
Research indicates that the genetic factors responsible for height are complex, involving multiple genes with additive effects. Studies published in journals such as Nature Genetics have identified several genetic variants that contribute to height, many of which are inherited from the father. Paternal height can often be a reliable indicator of a child’s potential growth pattern.
Key Factors Influencing Height
- Genetic Variants: Specific genes passed down from your father may enhance or limit growth potential, affecting overall stature.
- Hormonal Influence: Growth hormones, which are partly regulated by genetic factors, also play a significant role in determining height.
- Environmental Interaction: While genetics provide the blueprint, nutrition and overall health during childhood and adolescence can modify how these genetic factors are expressed.
Understanding these genetic influences can help you appreciate why your father’s height might be a strong predictor of your own. For more detailed insights on the genetics of height, check out the Harvard Health Blog.
Crooked Teeth: The Genetic Influence of Your Father on Dental Alignment

Dental traits, including the alignment of your teeth, can sometimes be traced back to your father’s genes. Although crooked teeth are influenced by both genetics and environmental factors such as oral habits and nutrition, several genetic markers linked to dental development may be inherited predominantly from your father.
The Role of Paternal Genes in Dental Formation
Genetics plays a significant role in determining the size, shape, and positioning of your teeth. Paternal genes can affect jaw structure and dental alignment, making crooked teeth a trait that many associate with their father’s genetic influence. Studies in the field of orthodontics suggest that inherited jaw size and dental arch shape can predispose individuals to malocclusion (improper alignment).
Factors Contributing to Crooked Teeth
- Jaw Structure: A smaller or asymmetrical jaw, often inherited from the father, can lead to overcrowding or misalignment of teeth.
- Tooth Size and Shape: Variations in the size and shape of teeth, influenced by genetics, can result in crooked appearances.
- Inherited Dental Patterns: Genetic predispositions can affect the timing of tooth eruption and the overall development of dental arches.
For further reading on how genetics impact dental health, visit Colgate’s Oral Health Center which offers valuable insights into orthodontic research and hereditary factors.
Gender Determination: The Crucial Role of Paternal Genes
One of the most definitive traits determined solely by your father is your gender. Unlike most characteristics that result from a blend of maternal and paternal genes, gender is decided at the moment of conception by the sperm.
How Gender is Determined
Biologically, gender is determined by the combination of sex chromosomes received from each parent. Women contribute an X chromosome, while men contribute either an X or a Y chromosome. If the sperm carries an X chromosome, the resulting offspring will be female (XX). Conversely, if the sperm carries a Y chromosome, the child will be male (XY). This means that the father’s genetic contribution is the deciding factor in determining the baby’s gender.
Paternal Influence on Gender
- Sperm Composition: The sperm produced by the father contains the crucial sex-determining chromosome, making him solely responsible for the gender of the child.
- Genetic Implications: The Y chromosome not only determines male gender but also carries genes that affect other traits and even aspects of male health.
This clear-cut role of paternal genetics in gender determination underscores the unique influence of the father in the inheritance process. For a more detailed explanation of gender determination and genetics, you can explore resources on Genetics Home Reference.
Dimples: A Fun and Unique Trait Often Linked to Paternal Genetics

Dimples are a charming and often-discussed trait that many believe are inherited from the father. While not all dimples are strictly passed down from the paternal side, there is a strong genetic component that can make this feature more common in some families.
The Science Behind Dimples
Dimples occur due to variations in the facial muscle structure, particularly in the zygomaticus major muscle, which is responsible for facial expressions. A small, inherited defect in this muscle can cause the skin to retract and form a dimple. Genetic studies suggest that the presence of dimples may have a dominant inheritance pattern, and anecdotal evidence often points to paternal lineage as the source.
Why Dimples Stand Out
- Facial Aesthetics: Dimples are often seen as a sign of beauty and charm, adding to the unique facial characteristics that may be inherited from your father.
- Genetic Variability: While both parents contribute to your genetic makeup, the appearance of dimples is sometimes more pronounced in families where the father has distinct dimples.
The presence of dimples not only adds to your unique appearance but also serves as a fun reminder of the subtle genetic influences passed down from your father. For more on the genetics of facial features, consider reading articles on WebMD.
Fingerprints: Unique Patterns Shaped by Paternal Genetic Blueprint
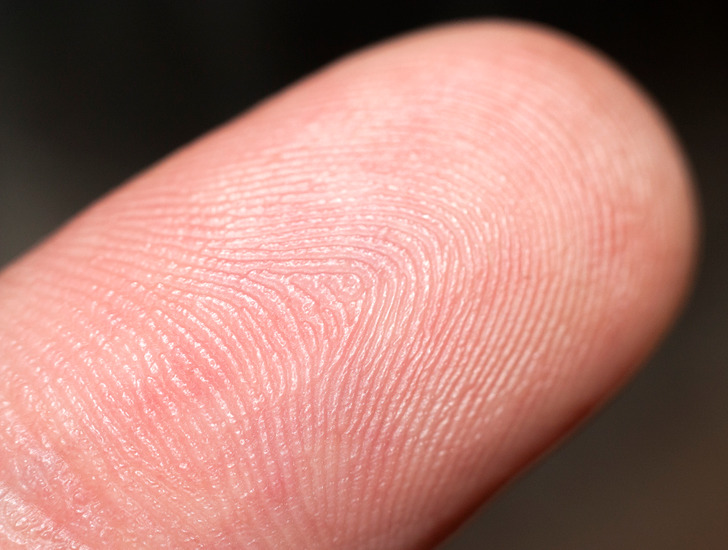

Fingerprints are one of the most fascinating examples of how genetics can create unique identifiers for each individual. Although the formation of fingerprints is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors during fetal development, research has shown that certain patterns may have a strong paternal influence.
The Genetic Basis of Fingerprints
Fingerprints develop in the womb and are determined by the complex interplay of genetic instructions and intrauterine conditions. While no single gene controls the formation of fingerprints, variations in certain genetic markers inherited from your father can influence the ridges and whorls that make up your fingerprint patterns. These unique patterns serve as a biological fingerprint, ensuring that no two individuals have identical prints.
Why Fingerprints Matter
- Security and Identification: Fingerprints are widely used in forensic science and security systems due to their uniqueness and reliability.
- Genetic Imprints: Although influenced by the environment, the genetic blueprint provided by your father plays a critical role in shaping these patterns, making them a fascinating aspect of human heredity.
For an in-depth look at the genetics behind fingerprints, you can refer to studies available on PubMed, which offer extensive research on the subject.
The Broader Picture: Understanding Paternal Inheritance
While the traits discussed above highlight some of the fascinating ways in which your father’s genes can influence your physical characteristics, it is important to note that genetic inheritance is a complex process. Many traits are the result of interactions between multiple genes from both parents, as well as environmental influences. However, certain characteristics, such as the determination of gender and specific genetic markers in traits like dimples and dental alignment, can often be traced directly to your father.
The Role of Genetic Testing and Research
Advancements in genetic testing and research have allowed us to better understand the intricate details of inheritance. Companies specializing in DNA testing, such as 23andMe and AncestryDNA, provide personalized insights into genetic traits, including those inherited from your father. These tests can offer a deeper understanding of your genetic makeup and reveal fascinating details about your ancestral lineage.
How Paternal Traits Shape Your Identity
The traits inherited from your father are more than just physical characteristics—they contribute significantly to your identity. Whether it’s the height you stand at, the unique pattern of your fingerprints, or even the dimples that give your smile a special charm, your father’s genetic legacy is woven into the fabric of who you are. Embracing these traits can help you appreciate the role of genetics in shaping your individuality and encourage further exploration into the fascinating world of heredity.
The Psychological Impact of Inherited Traits
Understanding that certain traits come from your father can also have a positive psychological impact. Recognizing these unique features can help foster a sense of identity and pride in your genetic heritage. It opens up conversations about family history and the shared characteristics that bind generations together.
Encouraging Genetic Literacy
In today’s world, having a basic understanding of genetics is increasingly important. From personalized healthcare to ancestry research, the knowledge of how traits are passed down can empower you to make informed decisions about your well-being. Educational resources such as those available through the National Institutes of Health (NIH) offer excellent material for those interested in diving deeper into genetic science.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Legacy of Paternal Inheritance
In summary, the traits you inherit from your father—ranging from height and crooked teeth to gender, dimples, and fingerprints—offer a fascinating glimpse into the complex interplay of genetics that shapes who you are. While the process of genetic inheritance involves contributions from both parents, the unique role of your father is evident in these specific characteristics.
Embracing the legacy of paternal inheritance means not only appreciating the physical traits passed down through generations but also acknowledging the deeper genetic connections that contribute to your overall identity. Whether you are curious about your family history, interested in genetic testing, or simply fascinated by the science behind inheritance, these insights into paternal traits serve as a reminder of the enduring impact of your father’s genes.
Stay informed by exploring credible sources like Mayo Clinic, WebMD, and Harvard Health, and consider genetic testing services to gain personalized insights into your genetic makeup. Understanding the traits that you inherit from your father not only deepens your knowledge of genetics but also connects you to the rich tapestry of your family’s history.
By delving into these five distinct traits, you gain a greater appreciation for the intricate ways in which genetics shape our lives—making every feature, every quirk, and every inherited characteristic a testament to the legacy of our fathers.
This article is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional genetic or medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a certified genetic counselor if you have concerns about genetic traits or health-related issues.
Preview photo credit depositphotos.com, PopularImages/depositphotos.com