Drinking water is essential for life and overall well-being, but like most things, too much of a good thing can lead to negative consequences. While hydration is key to maintaining health, overhydration—or water intoxication—can disturb the delicate balance of electrolytes in your body and cause serious health complications. In this in-depth article, we will explore the effects of excessive water consumption on your body, including potential risks such as bloating, swelling, nausea, overhydration symptoms, and muscle cramps. We’ll also provide practical advice on how to strike the right balance and prevent water-related health issues.
How Excessive Water Intake Affects Your Body: An Overview
Your body relies on water to regulate temperature, transport nutrients, and maintain cellular function. However, drinking too much water can dilute sodium levels in your blood, leading to a condition known as hyponatremia. Hyponatremia is characterized by low sodium levels, which can cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. Health experts warn that even those who lead an active lifestyle or are focused on detox and weight management might inadvertently risk overhydration if they consume water beyond their body’s needs.
Your Belly Might Get Bloated: Understanding Abdominal Distension
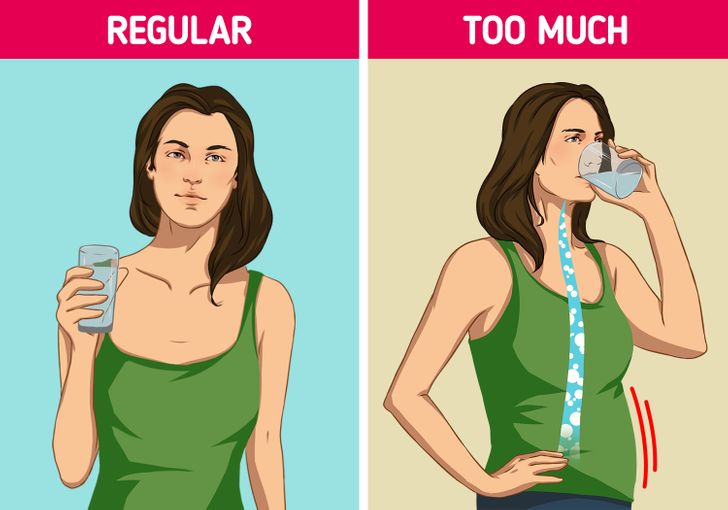
Excess water consumption can lead to abdominal bloating—a condition where the stomach appears distended and feels uncomfortable. When your body takes in more water than it can process, it causes fluid retention, which may lead to a visibly swollen belly. This is particularly concerning for individuals who are monitoring their weight or following specific dietary regimens.
What Causes Bloating from Excess Water?
Bloating is often the result of your body trying to balance fluid levels. Excess water disrupts the natural equilibrium, causing tissues and organs to swell. This can lead to a feeling of fullness or tightness in the abdomen.
Scientific Perspective:
According to Healthline, bloating is a common symptom of electrolyte imbalance. The rapid shift in fluid levels forces the body to hold on to more water, which can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful.
Prevention Tips:
Monitor your water intake relative to your body weight and physical activity. Consider using a water tracking app to stay within recommended hydration guidelines.
Bloating from overhydration is not only uncomfortable but also a visible sign that your body might be struggling with an excess of water. Recognizing this symptom early can help you adjust your habits and prevent more severe health issues.
Your Hands And Feet Might Swell: The Link Between Overhydration and Edema
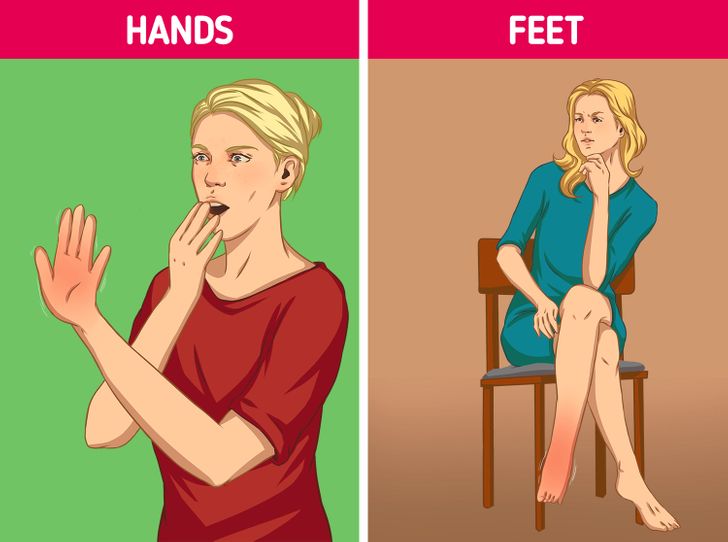
Another common sign of drinking too much water is swelling in the extremities—specifically, your hands and feet. Edema, the medical term for swelling, occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues, leading to puffiness and discomfort.
Why Does Edema Occur?
When your kidneys are overwhelmed by excess water, they may not filter the fluid efficiently. This leads to an accumulation of water in the peripheral tissues, resulting in swelling. Edema is not only a cosmetic concern; it can also be indicative of an underlying electrolyte imbalance.
Medical Insights:
The Mayo Clinic explains that edema can result from a variety of conditions, including overhydration. Although typically associated with heart or kidney issues, overhydration-induced edema is a less common but important signal of excessive water intake.
Managing Swelling:
If you notice swelling in your hands or feet, consider reducing your water intake and consulting a healthcare professional to evaluate your electrolyte levels. Incorporating natural diuretics such as cucumber or dandelion tea may also help in managing mild cases.
Swelling in your extremities is not only a physical discomfort but can also interfere with your daily activities. Monitoring such symptoms is crucial for those who aim to optimize their health and avoid the pitfalls of overconsumption.
You Might Experience Nausea: The Gut Reaction to Too Much Water
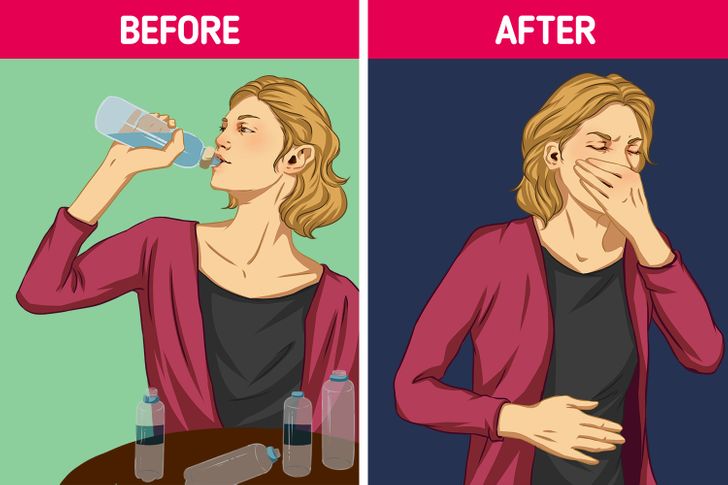
Nausea is another potential symptom of excessive water consumption. When you ingest large volumes of water in a short period, it can overwhelm your digestive system and lead to an upset stomach.
Mechanism Behind Nausea:
Drinking water rapidly can dilute the stomach’s natural acids, which are essential for digestion. This dilution can disrupt the digestive process, causing the stomach to work harder and leading to feelings of nausea. In some cases, severe overhydration can even result in vomiting, as the body attempts to expel the excess fluid.
Clinical Perspective:
Medical sources such as WebMD note that nausea is a common response to an imbalance in electrolytes and digestive fluids. It serves as a warning sign that your body is trying to restore its normal functioning.
How to Prevent Nausea from Overhydration:
Instead of chugging large amounts of water quickly, sip water steadily throughout the day. Balance your water intake with proper nutrition that supports electrolyte replenishment, including potassium-rich foods like bananas and leafy greens.
For individuals experiencing regular bouts of nausea, it is crucial to assess your water consumption habits. Moderation and balanced intake can help mitigate these symptoms and ensure that your digestive system remains healthy.
You Might Get Symptoms Of Overhydration: Recognizing Water Intoxication

Overhydration, or water intoxication, occurs when the balance between water and electrolytes in your body is severely disrupted. Recognizing the symptoms early can help you avoid dangerous complications.
Defining Overhydration:
Overhydration is more than just drinking too much water—it’s a state where your blood’s sodium levels become dangerously low, leading to a cascade of adverse symptoms. Key indicators include confusion, headaches, and in extreme cases, seizures.
Symptoms to Watch For:
Early symptoms of water intoxication include bloating, swelling, and nausea. As the condition worsens, you might experience headaches, disorientation, and muscle weakness. Immediate medical attention is recommended if these symptoms persist.
Expert Advice:
Medical News Today emphasizes that water intoxication is a rare but potentially fatal condition. Experts advise balancing fluid intake with the body’s needs and being cautious during activities that increase water consumption, such as intense physical exercise.
Prevention Strategies:
To avoid overhydration, it’s important to listen to your body’s thirst signals and adjust your water intake according to your activity level and environmental conditions. Consulting with a nutritionist or healthcare provider can also provide personalized hydration recommendations.
Recognizing the signs of overhydration early on is vital. By being aware of the symptoms and maintaining a balanced water intake, you can protect yourself from the serious health risks associated with water toxicity.
Your Muscles Cramp Easily: The Impact on Physical Performance
One of the less obvious yet concerning symptoms of excessive water intake is muscle cramping. Muscles rely on a delicate balance of electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, to function properly. When this balance is disrupted by overhydration, muscle cramps can become more frequent and severe.
Understanding Muscle Cramps:
Muscle cramps occur when the muscles involuntarily contract and fail to relax. These cramps are not only painful but can significantly impair physical performance. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are particularly at risk, as maintaining electrolyte balance is crucial for peak performance.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Drinking too much water can wash away essential electrolytes, leading to an imbalance that manifests as muscle cramps. Research on hydration and physical performance from Runner’s World highlights that athletes must carefully balance water intake with electrolyte consumption, especially during prolonged exercise.
Preventing Cramps:
To prevent muscle cramps, ensure that you are not only drinking water but also replenishing electrolytes through balanced meals or supplements. Foods rich in magnesium, calcium, and potassium can support muscle function and prevent cramps.
Recovery and Treatment:
If you experience muscle cramps frequently, it may be necessary to reassess your hydration strategy. Incorporating natural electrolyte drinks or sports beverages in moderation can help restore the balance and improve recovery times.
Muscle cramps due to overhydration can hinder your ability to perform daily tasks and engage in physical activities. Prioritizing both water and electrolyte balance is essential for maintaining optimal muscle function and overall health.
Striking the Right Balance: Tips for Optimal Hydration
While the dangers of overhydration are significant, it’s important to remember that water is essential for a healthy body. The goal is to strike a balance between staying hydrated and avoiding the risks of excessive consumption. Here are some tips to help you maintain optimal hydration:
Listen to Your Body:
Thirst is a natural indicator of your body’s hydration needs. Drink water when you feel thirsty and avoid forcing excessive water intake.
Monitor Your Intake:
Use water tracking apps or set reminders throughout the day to help you keep track of your fluid consumption. This is especially important if you’re active or in a hot climate.
Balance with Electrolytes:
Ensure that your diet includes foods rich in electrolytes, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. In cases of intense physical activity, consider electrolyte-enhanced beverages.
Consult Professionals:
If you’re uncertain about how much water you should be drinking, consult a nutritionist or healthcare provider who can offer personalized advice based on your body’s needs and lifestyle.
Adjust for Activity and Climate:
Remember that your hydration needs may vary depending on your activity level and the climate. In hot weather or during vigorous exercise, it’s crucial to balance water intake with proper electrolyte replenishment.
By following these practical tips, you can avoid the risks of overhydration while ensuring that your body receives the essential fluids it needs to function properly.
The Science Behind Water Toxicity and Health
Understanding the science of water toxicity can empower you to make better hydration decisions. Overhydration leads to a dilution of sodium levels in the blood, a condition medically known as hyponatremia. This condition can result in symptoms that range from mild discomfort to severe neurological damage.
Hyponatremia Explained:
Sodium is a critical electrolyte that helps regulate water balance in and around your cells. When you consume too much water, your kidneys are unable to excrete the surplus, resulting in low sodium levels. Hyponatremia can cause cellular swelling, particularly in the brain, leading to serious symptoms like confusion, seizures, and even coma in extreme cases.
Medical Insights and Recommendations:
Reputable sources such as Mayo Clinic and WebMD have published extensive resources on hyponatremia, emphasizing the importance of a balanced water intake. These sources suggest that while hydration is crucial, moderation is key.
Implications for Daily Health:
Being informed about the science behind overhydration allows you to tailor your daily water intake based on your personal needs, activity level, and health goals. This knowledge is particularly valuable in today’s health-conscious environment, where many individuals strive for natural detox and optimal performance.
Understanding water toxicity is not just for athletes or health enthusiasts—it’s relevant to anyone looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle. By recognizing the signs of overhydration, you can make informed decisions about your water consumption.
Practical Recommendations for Healthy Hydration
Achieving a healthy hydration balance is essential for overall wellness. Here are some additional practical recommendations to help you stay within the optimal range:
Use a Hydration Calculator:
Numerous online tools can help estimate your daily water requirements based on factors such as age, weight, and activity level. These calculators can guide you in setting realistic hydration goals.
Include Electrolyte-Rich Foods:
Incorporate foods such as bananas, avocados, spinach, and yogurt into your diet. These foods provide essential nutrients that complement your water intake and support muscle function.
Adjust According to Lifestyle:
If you exercise regularly or live in a warmer climate, you may need to increase your water intake slightly. However, always balance this with electrolyte intake to prevent an imbalance.
Monitor Physical Signals:
Pay attention to signs such as persistent bloating, swelling, and muscle cramps. If you experience these symptoms, it might be time to reassess your hydration habits.
Seek Professional Guidance:
If you have any preexisting health conditions or are uncertain about your hydration needs, consult with a healthcare provider or nutrition expert who can provide tailored advice.
These practical steps are designed to help you navigate the fine line between proper hydration and overhydration, ensuring that your body functions at its best without risking electrolyte imbalances.
Final Thoughts: Prioritizing Health Over Excess
While water is undeniably essential, the trend toward overconsumption in the pursuit of health benefits must be approached with caution. By understanding the potential risks associated with excessive water intake—such as bloating, swelling, nausea, and muscle cramps—you can take proactive steps to ensure that your hydration habits support your overall health.
Maintaining a balanced approach to hydration involves not only drinking water when needed but also listening to your body’s signals, monitoring intake, and supplementing with essential electrolytes. This balanced approach is critical in today’s fast-paced world, where health optimization and natural detox trends continue to gain popularity.
For further reading on the science of hydration and electrolyte balance, consider exploring reputable resources such as Healthline and Medical News Today.
By staying informed and attentive to your body’s needs, you can enjoy the benefits of proper hydration without risking the severe complications that come with overhydration. Remember, your health is your most valuable asset—maintain it wisely.