Sugar is ubiquitous in our daily diets—present in soft drinks, baked goods, and even savory foods. While it satisfies our cravings for sweetness, mounting scientific evidence reveals that excessive sugar consumption can lead to severe health consequences. In this comprehensive guide, we explore four dangerous properties of sugar that many of us are unaware of. We’ll delve into how sugar accelerates skin aging, promotes chronic inflammation, contributes to cardiovascular diseases, and even impacts our mental health. Backed by credible research and expert opinions, this article is designed to inform and empower you to make healthier choices.
Sugar Accelerates Skin Aging: Uncovering the Hidden Effects on Your Complexion
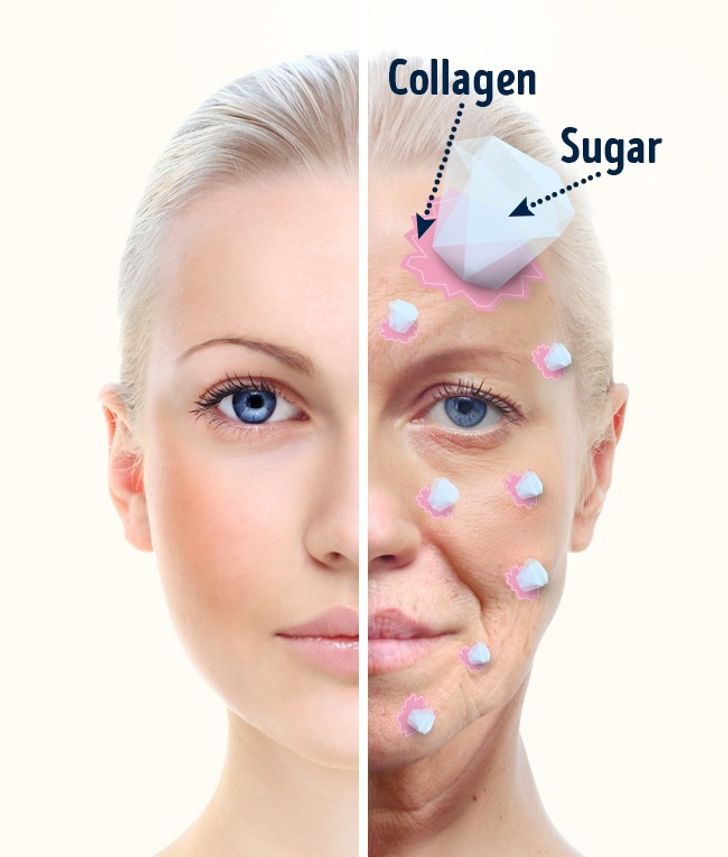
Our skin is our largest organ, and it reflects what we consume on the inside. Excess sugar can have a profound effect on skin health, accelerating the aging process and leading to premature wrinkles and sagging.
The Science Behind Glycation and Skin Aging
When you consume high amounts of sugar, a process called glycation occurs. This chemical reaction occurs when sugar molecules attach to proteins, such as collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. Over time, glycation damages these proteins, leading to reduced skin elasticity and the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. According to Healthline, glycation is a major contributor to skin aging, making it a significant concern for those looking to maintain youthful skin.
Impact on Skin Texture and Hydration
Sugar doesn’t just cause wrinkles—it also affects the overall texture and hydration of the skin. When collagen and elastin are compromised, your skin loses its ability to retain moisture, leading to dryness and an uneven complexion. This can result in dull, tired-looking skin that is more prone to damage and irritation. Dermatologists emphasize the importance of reducing sugar intake as part of a comprehensive skincare routine to slow down the aging process and improve overall skin health.
Sugar Promotes Inflammation: How Excessive Sugar Intake Fuels Chronic Inflammatory Responses
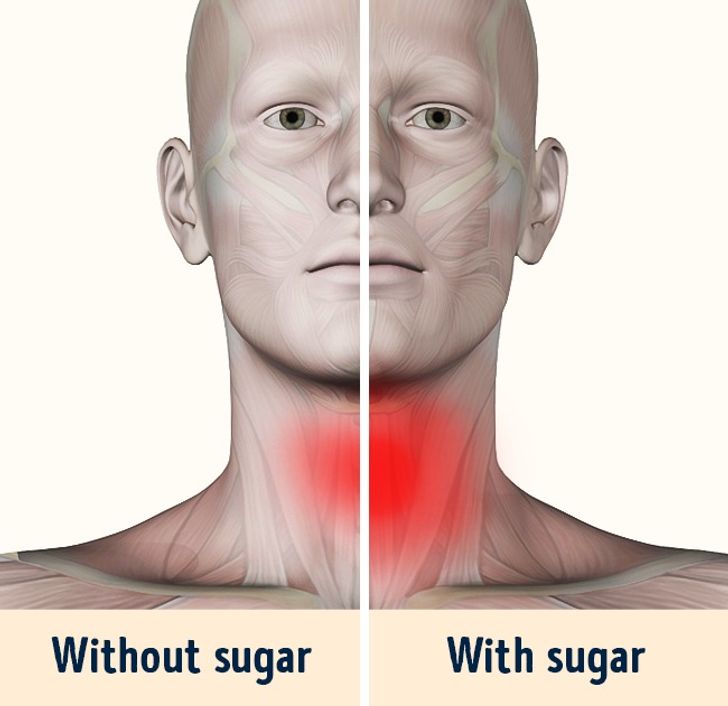
Chronic inflammation is a silent enemy that can pave the way for numerous health issues, from joint pain to more serious conditions like arthritis and autoimmune diseases. Sugar is one of the leading dietary culprits in triggering and sustaining inflammatory responses in the body.
Understanding Inflammation and Its Consequences
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to a host of health problems. High sugar intake leads to increased production of inflammatory markers in the body. Research published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has shown that diets high in sugar can lead to elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and other cytokines, which are indicators of chronic inflammation.
The Link Between Sugar and Autoimmune Conditions
For individuals with autoimmune conditions, chronic inflammation can be particularly detrimental. Excess sugar consumption has been linked to the exacerbation of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. By triggering an overactive immune response, sugar not only worsens existing conditions but also increases the risk of developing new inflammatory issues. Cutting back on sugar can help reduce the severity of inflammation and potentially alleviate some of the symptoms associated with these disorders.
Sugar Causes Cardiovascular Diseases: Understanding the Link Between Sugar and Heart Health
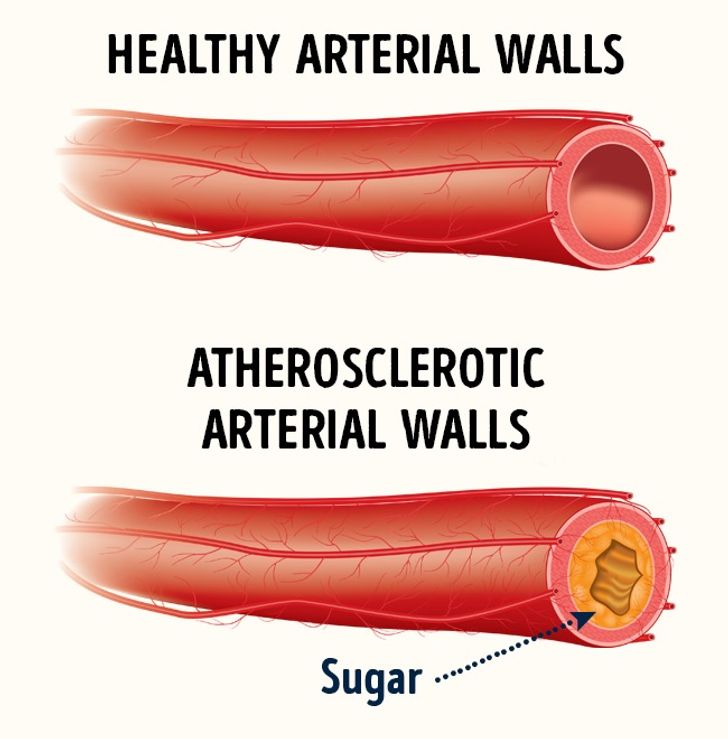
The impact of sugar on cardiovascular health is a critical concern, as heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Excessive sugar consumption can lead to a variety of heart-related issues, from increased blood pressure to the development of atherosclerosis.
How Sugar Affects Heart Health
When you consume too much sugar, it can lead to higher levels of triglycerides, lower levels of HDL (good cholesterol), and increased inflammation—all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Studies have shown that diets high in added sugars can increase the risk of heart disease by contributing to weight gain, insulin resistance, and high blood pressure. The Mayo Clinic highlights that excessive sugar intake is a significant risk factor for the development of heart disease, emphasizing the need for dietary moderation.
The Role of Sugar in Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions that include high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels—is strongly linked to high sugar consumption. This syndrome increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. By reducing sugar intake, you can improve your metabolic profile and reduce the likelihood of developing these serious health issues.
Sugar and Mental Health: How High Sugar Intake Impacts Your Brain and Mood
It might come as a surprise that sugar can also have a profound impact on mental health. Beyond physical health, excessive sugar consumption has been linked to mood swings, cognitive decline, and even an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
The Neurological Impact of Sugar
Sugar consumption triggers a rapid spike in blood glucose levels, which can lead to a temporary surge of energy followed by a sharp drop. This rollercoaster effect can cause fluctuations in mood and energy levels. Over time, these swings can affect brain function and lead to mental health issues. Research from Harvard Health Publishing suggests that diets high in sugar may impair cognitive function and contribute to an increased risk of developing mental health disorders.
Sugar Addiction and Behavioral Effects
The term “sugar addiction” is often used to describe the compulsive consumption of sugary foods, which can have a similar effect on the brain as addictive substances. High sugar intake can lead to the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. However, repeated stimulation of this pathway can lead to a dependence on sugar, making it difficult to break the habit. This cycle of craving and reward can contribute to anxiety, irritability, and even depressive symptoms.
Practical Tips for Reducing Sugar Intake and Improving Overall Health
Now that we’ve explored the dangerous properties of sugar—from its impact on skin aging and inflammation to its effects on cardiovascular and mental health—what can you do to protect yourself? Here are some actionable strategies to help reduce your sugar consumption and improve your overall health.
Read Labels and Identify Hidden Sugars
Many processed foods contain added sugars that are not immediately obvious. Learn to read labels carefully and identify ingredients such as high-fructose corn syrup, maltose, and sucrose. Reducing your intake of these hidden sugars is a crucial step in lowering your overall sugar consumption.
Embrace a Whole Foods Diet
A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods can help you avoid the pitfalls of high sugar intake. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Not only does this support better overall health, but it also provides essential nutrients that can help combat the negative effects of sugar.
Choose Natural Sweeteners Wisely
If you need to satisfy your sweet tooth, opt for natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit, which have a lower glycemic index than refined sugar. These alternatives can help you enjoy a hint of sweetness without the severe health repercussions associated with traditional sugar.
Stay Hydrated and Exercise Regularly
Water is essential for overall health and can help flush excess sugar from your system. Regular physical activity also aids in maintaining a healthy weight and improving metabolic health. Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can mitigate some of the adverse effects of sugar on your heart and brain.
Consult with Health Professionals
For personalized advice, consider consulting with healthcare professionals or nutritionists. Trusted sources such as WebMD and Mayo Clinic offer comprehensive insights into the impact of sugar on health and provide evidence-based recommendations for dietary adjustments.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Health by Tackling Sugar
Sugar may be a staple in modern diets, but its dangerous properties—ranging from accelerating skin aging and promoting chronic inflammation to increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and impacting mental health—cannot be ignored. By understanding these risks and taking proactive steps to reduce your sugar intake, you can significantly improve your overall health and quality of life.
Making informed dietary choices is essential for long-term well-being. Embracing a balanced, whole foods diet, staying active, and seeking professional guidance when needed are all crucial strategies to combat the harmful effects of sugar. Remember, small changes in your daily habits can lead to substantial health benefits over time.
By sharing the science behind sugar’s hidden dangers and offering practical tips for healthier living, we hope to empower you to take charge of your health. Whether you’re looking to enhance your skin’s appearance, reduce inflammation, protect your heart, or improve your mental clarity, understanding the impact of sugar is the first step towards a healthier future.
For additional information and expert advice on reducing sugar intake and managing its effects on your health, be sure to explore resources from reputable organizations like Harvard Health Publishing, Healthline, and the Mayo Clinic.
Take control of your diet today, and your body will thank you tomorrow. The journey to a healthier lifestyle begins with understanding the risks and making informed choices. It’s time to break free from sugar’s grip and embrace a life of vitality and well-being.