Japan is renowned for its long and healthy population, and a key component of this success story is the humble grain—rice. As a dietary staple, rice is celebrated not only for its versatility and taste but also for its remarkable health benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into how eating rice helps the Japanese live so long by exploring its multifaceted role in promoting wellness.
From aiding weight loss and heart health to regulating blood sugar, enhancing digestion, supporting the nervous system, and fueling energy levels, rice is much more than just a side dish. Let’s explore the remarkable benefits of rice and understand why it is a cornerstone of the Japanese diet and lifestyle.
It May Help You Lose Weight: Rice as a Weight Management Ally

Rice, particularly when consumed in its whole grain or brown rice form, plays a significant role in weight management. Despite being a carbohydrate-rich food, rice is an essential part of the Japanese diet and is associated with a balanced lifestyle that promotes healthy body weight.
How Rice Supports Weight Loss
Low Glycemic Index:
Brown rice and other whole-grain rice varieties have a lower glycemic index compared to refined carbohydrates. This means that they release glucose more slowly into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar and reducing hunger pangs. This controlled energy release helps in maintaining satiety and curbing overeating.
Fiber-Rich Composition:
Rice, especially brown rice, is high in dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness. Increased fiber intake is linked to reduced overall calorie consumption, making it easier to lose weight.
Balanced Macronutrients:
Incorporating rice as part of a balanced meal that includes lean proteins and vegetables ensures that you receive a well-rounded nutrient profile without excessive calories.
Practical Tips for Weight Management with Rice
Portion Control:
Enjoy rice in moderate portions, pairing it with plenty of vegetables and lean protein to create a balanced meal.
Choose Whole Grains:
Opt for brown rice, black rice, or other whole-grain varieties that are richer in fiber and nutrients compared to white rice.
Mindful Eating:
Incorporate mindful eating practices when consuming rice-based meals. This can help you appreciate the food and avoid overeating.
For more detailed advice on weight management, check out Healthline’s weight loss strategies.
It Keeps the Heart Healthy: Rice and Cardiovascular Benefits
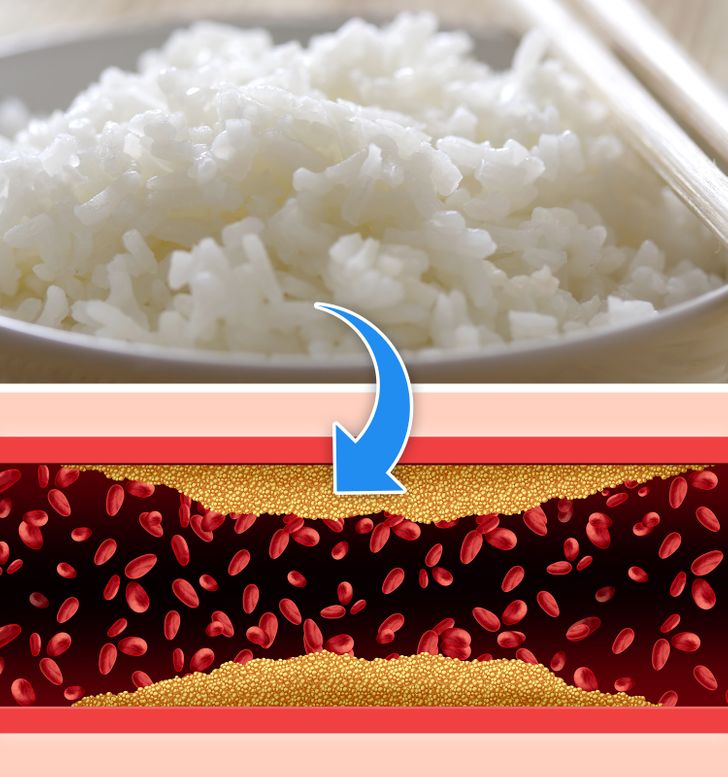
A heart-healthy diet is vital for long-term wellness, and rice is an important component of the Japanese dietary pattern that contributes to cardiovascular health.
Rice and Heart Health
Low in Saturated Fat:
Rice is naturally low in saturated fat, which is beneficial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. Diets low in saturated fats are known to reduce the risk of heart disease.
Rich in Antioxidants and Nutrients:
Whole-grain rice varieties are loaded with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals such as magnesium, which play a crucial role in maintaining heart health. Magnesium, for instance, helps regulate blood pressure and maintain a healthy heart rhythm.
Balanced Energy Source:
As a complex carbohydrate, rice provides a steady source of energy without causing drastic fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Stable energy levels contribute to overall heart health by preventing the spikes that can lead to increased blood pressure and stress on the cardiovascular system.
Heart-Healthy Eating Habits
Combine with Healthy Fats:
Pair rice with heart-healthy fats like those found in fish, nuts, and olive oil to further support cardiovascular health.
Incorporate Fresh Vegetables:
Create balanced meals by adding a variety of vegetables to your rice dishes. Vegetables add fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants that bolster heart health.
Monitor Sodium Intake:
While rice itself is low in sodium, be mindful of high-sodium sauces and seasonings that can accompany rice dishes.
For more heart-healthy tips and research, visit American Heart Association’s website.
It Keeps High Blood Sugar at Bay: Rice and Blood Sugar Control

Managing blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and longevity, and rice—when chosen wisely—can play a supportive role in maintaining stable glucose levels.
How Rice Contributes to Blood Sugar Regulation
Slow Digesting Carbohydrates:
The complex carbohydrates in brown and whole-grain rice are digested slowly, resulting in a gradual release of sugar into the bloodstream. This slow digestion helps prevent the rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar that are often associated with refined carbohydrates.
Fiber Content:
High-fiber rice varieties not only aid in digestion but also help regulate blood sugar by slowing the absorption of sugars. This leads to more consistent energy levels throughout the day.
Portion Control and Balance:
Eating rice as part of a balanced meal that includes proteins and healthy fats further moderates blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Tips for Using Rice in a Diabetes-Friendly Diet
Opt for Brown or Black Rice:
These varieties have a lower glycemic index than white rice and provide additional nutrients that support overall health.
Combine with Protein and Fiber:
Balance your rice meals with lean proteins and fiber-rich vegetables to help stabilize blood sugar.
Monitor Serving Sizes:
Be mindful of portion sizes to ensure that you are not consuming excessive carbohydrates in one meal.
For more information on blood sugar management, explore WebMD’s guide on managing diabetes.
It Helps Digestion: The Digestive Benefits of Rice
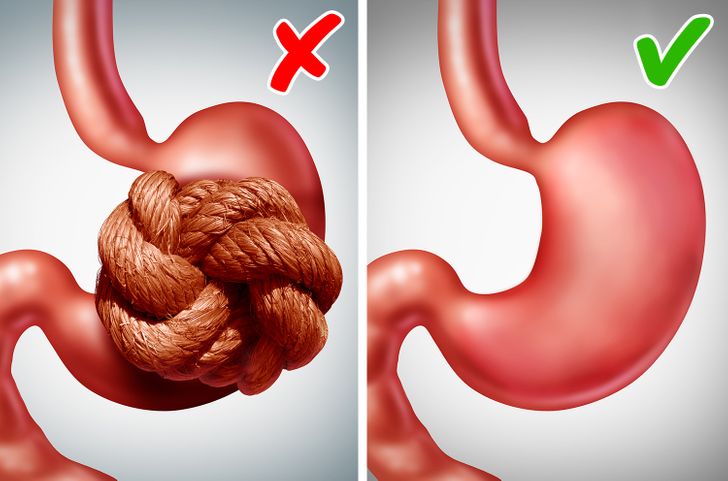
Rice is widely recognized for its gentle effect on the digestive system, making it a preferred food for people of all ages, particularly those with sensitive stomachs. Its ease of digestion and soothing properties have contributed significantly to its popularity in Japanese cuisine.
How Rice Enhances Digestive Health
Easily Digestible:
Rice is a low-fiber, bland carbohydrate that is easy on the stomach. This makes it an ideal food for individuals experiencing gastrointestinal distress or recovering from an illness.
Soothing Effect:
The soft texture of cooked rice provides a soothing effect on the digestive tract, helping to alleviate symptoms of conditions such as gastritis and diarrhea.
Supports a Healthy Gut:
While rice itself is low in fiber, it can be combined with other nutrient-dense, fiber-rich foods to promote overall gut health and a balanced digestive system.
Best Practices for Digestive Health with Rice
Cook Rice Properly:
Ensure that rice is cooked thoroughly to enhance its digestibility. Overcooked rice is often softer and easier on the stomach.
Combine with Probiotic Foods:
Pair rice with probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt or fermented vegetables to boost gut health.
Stay Hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water with your meals aids in digestion and helps prevent constipation.
For additional tips on maintaining digestive health, refer to Mayo Clinic’s digestive health resources.
It Improves Nervous System Health: Rice as a Neuroprotective Food

Emerging research suggests that the nutrients found in rice, especially whole-grain varieties, may have a positive impact on nervous system health. A well-functioning nervous system is crucial for cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall mental well-being.
The Neuroprotective Properties of Rice
Rich in B Vitamins:
Rice, particularly brown rice, is a good source of B vitamins such as thiamine, niacin, and riboflavin. These vitamins are essential for maintaining healthy nerve cells and supporting brain function.
Antioxidant Benefits:
The antioxidants in rice help protect nerve cells from oxidative stress, which can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases. This protective effect supports long-term cognitive health.
Energy Supply to the Brain:
As a complex carbohydrate, rice provides a steady stream of glucose—the brain’s primary source of energy. Consistent energy levels are critical for maintaining focus, memory, and overall cognitive performance.
Enhancing Nervous System Health with Rice
Integrate with Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Combine rice with foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish or flaxseeds, to further support brain health and reduce inflammation.
Balanced Diet Approach:
Incorporate a variety of nutrient-rich foods alongside rice to ensure a comprehensive intake of vitamins and minerals necessary for nervous system maintenance.
Regular Exercise:
Physical activity boosts blood flow to the brain, complementing the steady energy supply from rice for enhanced cognitive function.
For more on the relationship between diet and brain health, visit Harvard Health Publishing’s nutrition and brain function articles.
It Fuels Energy Levels: Sustained Energy with Rice

Energy is the cornerstone of an active, productive life, and rice plays a pivotal role in providing sustained energy. This simple, yet nutrient-rich food is a key component of the Japanese diet, ensuring that the body remains fueled throughout the day.
How Rice Boosts Energy Levels
Complex Carbohydrates:
Rice is a complex carbohydrate that provides a slow and steady release of energy. Unlike simple sugars that cause quick spikes and crashes, the energy from rice is long-lasting, supporting sustained physical and mental activity.
Glycogen Storage:
Carbohydrates from rice are stored as glycogen in the muscles and liver, which can be utilized during periods of physical exertion. This is particularly beneficial for athletes and active individuals.
Nutrient Density:
Brown rice and other whole-grain varieties are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber that collectively contribute to overall energy production and metabolic efficiency.
Tips for Maximizing Energy with Rice
Combine with Protein:
Pair rice with lean protein sources, such as chicken, tofu, or legumes, to create balanced meals that sustain energy and support muscle recovery.
Include a Variety of Vegetables:
Adding vegetables to your rice dishes not only increases the nutrient profile but also provides additional fiber, further aiding in sustained energy release.
Regular Meals:
Consuming rice as part of regular meals throughout the day can help maintain consistent energy levels and prevent the mid-day slump.
For more energy-boosting dietary strategies, explore Verywell Fit’s tips on sustaining energy.
Integrating Rice into a Balanced Lifestyle for Longevity
The Japanese diet is celebrated for its emphasis on balance, variety, and nutrient-dense foods, with rice at its core. Incorporating rice into your daily diet can be a powerful strategy for promoting longevity and overall well-being.
Holistic Benefits of a Rice-Centric Diet
Cultural and Social Benefits:
The act of sharing meals centered around rice fosters community and social interaction, which are essential components of mental health and longevity.
Balanced Nutrition:
Rice serves as a versatile base that can be paired with a wide range of nutrient-rich foods, from vegetables and proteins to healthy fats. This balance ensures a comprehensive nutrient intake that supports every aspect of health.
Sustainable Eating Habits:
As a staple food, rice is affordable, widely available, and environmentally sustainable. Its inclusion in a balanced diet supports long-term health and can contribute to reducing chronic diseases associated with poor dietary choices.
Practical Ways to Enjoy Rice Daily
Traditional Japanese Meals:
Embrace the Japanese approach by incorporating rice into meals that include a variety of side dishes, such as miso soup, grilled fish, and pickled vegetables.
Modern Recipes:
Experiment with modern recipes that fuse traditional and contemporary flavors—think rice bowls with lean proteins, fresh vegetables, and healthy sauces.
Mindful Eating Practices:
Adopt mindful eating habits by savoring each bite and appreciating the simplicity and nutritional value of rice-based meals.
For further reading on balanced nutrition and sustainable diets, visit EatRight.org by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Rice for a Longer, Healthier Life
Rice has long been a cornerstone of the Japanese diet, and its benefits extend far beyond being a simple carbohydrate. From aiding weight management and promoting heart health to stabilizing blood sugar, supporting digestion, enhancing nervous system function, and fueling energy, rice is a versatile, nutrient-dense food that plays a crucial role in the longevity and health of the Japanese people.
By integrating rice into your diet in a balanced and mindful way, you can harness these powerful benefits to support your own health and well-being. Whether you choose brown rice for its extra fiber and nutrients or enjoy traditional Japanese meals that celebrate the simplicity of rice, this staple food offers a proven path to a healthier, longer life.
Remember, the key to achieving lasting health is balance. Pair rice with a variety of nutrient-rich foods, engage in regular physical activity, and adopt mindful eating practices to maximize the benefits of this remarkable food. With consistency and careful planning, you can incorporate the timeless wisdom of the Japanese diet into your daily routine and set the stage for a vibrant, healthy future.
For more expert insights and practical tips on maintaining a balanced diet, consult trusted resources like Harvard Health Publishing and Mayo Clinic. Embrace the transformative power of rice and discover how this simple grain can be the key to unlocking a longer, healthier life—one meal at a time.









