In recent years, emerging scientific research has revealed an intriguing connection between the composition of gut bacteria and waist size. The balance of microorganisms in our digestive system, commonly referred to as gut flora or gut microbiota, not only plays a pivotal role in digestion but also influences metabolic health, inflammation levels, and even body weight. In this article, we will explore how your gut bacteria may affect your waist size, the science behind this connection, and effective strategies to improve your gut health for long-term wellness.
Modern lifestyles, dietary habits, and stress levels have dramatically impacted the diversity of our gut flora. This blog post dives deep into the intricate relationship between gut bacteria and weight management. We will also reference authoritative sources like Harvard Health and Mayo Clinic for a comprehensive understanding of this evolving field.
Gut Flora 101: Understanding the Basics of Your Microbiome
The human gut is home to trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi collectively known as the microbiome. This complex ecosystem plays a vital role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and defending against pathogens. The balance and diversity of these microorganisms can influence how efficiently our bodies process food and store energy.
What Is Gut Flora?
Gut flora refers to the community of bacteria that resides in our intestines. These bacteria are involved in synthesizing vitamins, regulating the immune system, and even communicating with the brain through the gut-brain axis. Research has shown that a diverse gut microbiome is associated with better overall health, while an imbalance (often referred to as dysbiosis) can contribute to a range of health issues, including obesity and inflammatory diseases.
Key Functions of the Gut Microbiome:
Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: Beneficial bacteria help break down complex carbohydrates and fibers, aiding in the extraction of essential nutrients.
Immune System Support: A robust gut microbiome trains the immune system to differentiate between harmful pathogens and non-threatening substances.
Metabolic Regulation: The gut microbiota influences metabolic processes, impacting how the body stores fat and burns calories.
For further details on the functions and importance of gut flora, check out this comprehensive article from NIH.
The Crucial Role of Gut Bacteria in Human Health
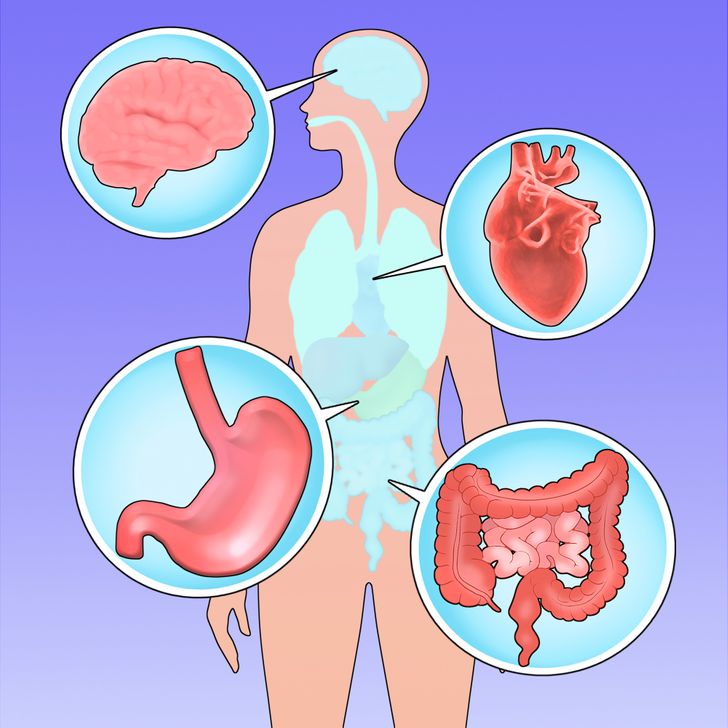
Understanding the role of gut bacteria in our overall health is essential for appreciating their impact on waist size and metabolic function. The gut microbiome affects numerous bodily systems, from digestion and immune response to hormonal balance and inflammation control.
Impact on Metabolism and Weight Management:
Several studies have indicated that individuals with a diverse and balanced gut microbiome tend to have better metabolic profiles. This includes improved insulin sensitivity and lower levels of systemic inflammation, both of which are critical factors in maintaining a healthy weight. Conversely, an imbalance in gut bacteria may lead to increased fat storage, particularly around the waistline.
Gut-Brain Connection:
The gut and brain communicate through a complex network known as the gut-brain axis. This bi-directional communication system means that changes in gut bacteria can influence mood, behavior, and even appetite regulation. For instance, some strains of bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which are known to have anti-inflammatory effects and may help regulate hunger hormones.
Inflammation and Chronic Disease:
Chronic low-grade inflammation is often a precursor to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease. An imbalance in gut flora can trigger inflammatory responses, contributing to the development of these conditions. By maintaining a healthy balance of bacteria, you can potentially reduce the risk of these inflammation-related disorders.
For more scientific insights into the health implications of gut bacteria, explore resources available at Mayo Clinic and Harvard Health Publishing.
How Gut Bacteria Impact Your Waist Size & Metabolic Health
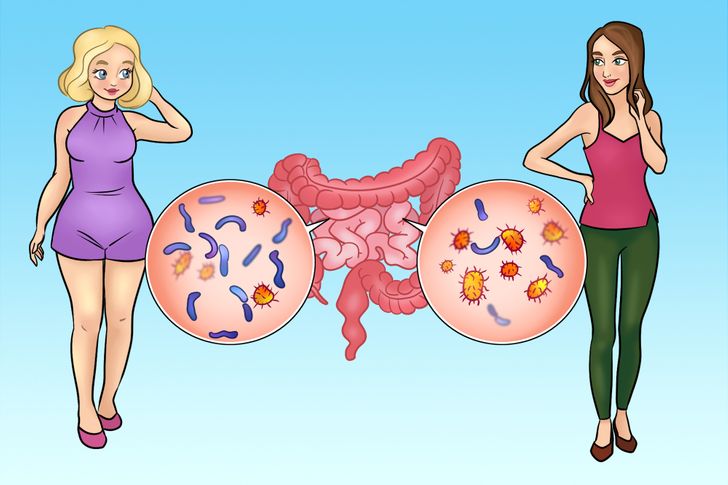
Recent research highlights a fascinating connection between the composition of gut bacteria and body fat distribution, particularly around the waist. This section delves into the mechanisms by which gut microbiota can influence waist size and overall metabolic health.
Mechanisms Linking Gut Bacteria to Waist Size:
Hormonal Regulation: Gut bacteria interact with the endocrine system, influencing hormones such as leptin and ghrelin that control appetite and satiety. An imbalance in these hormones can lead to overeating and weight gain, particularly around the midsection.
Energy Harvesting: Certain bacteria are more efficient at extracting calories from food. An overabundance of these bacteria might lead to an increased energy harvest, contributing to fat storage.
Inflammatory Response: An imbalanced gut microbiome can lead to increased intestinal permeability (often referred to as “leaky gut”), which allows toxins to enter the bloodstream and trigger systemic inflammation. This inflammation is closely linked to abdominal obesity.
Scientific Studies and Findings:
Multiple studies have examined the link between gut bacteria and obesity. For instance, research published by Nature has demonstrated that certain bacterial profiles are prevalent in individuals with higher waist circumferences compared to lean individuals. These studies suggest that manipulating the gut microbiota through diet, probiotics, and lifestyle changes can be a promising approach to managing weight.
For a detailed scientific overview, consider reading the research findings on gut bacteria at ScienceDirect.

Effective Strategies to Prevent Gut-Related Health Issues
Given the profound impact that gut bacteria have on waist size and overall health, it is essential to adopt strategies that promote a balanced gut microbiome. Here are some evidence-based practices to improve your gut health and potentially mitigate related health issues.
1. Optimize Your Diet for Gut Health
Your diet is one of the most powerful tools for shaping your gut microbiome. Focus on:
High-Fiber Foods: Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial bacteria in your gut.
Fermented Foods: Incorporate foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, which contain live probiotics that help balance your gut flora.
Healthy Fats: Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which have anti-inflammatory properties that benefit gut health.
For a comprehensive guide on dietary tips, visit Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.

2. Consider Probiotic and Prebiotic Supplements
In cases where dietary changes are not sufficient, probiotic supplements can help restore balance in the gut microbiota. Prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, serve as food for the beneficial bacteria. When choosing supplements, look for those with clinically proven strains and check with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
3. Maintain a Consistent Exercise Routine
Regular physical activity has been linked to a more diverse and robust gut microbiome. Exercise helps reduce inflammation, improves metabolic health, and supports overall weight management. Even moderate exercise, such as walking or cycling, can have positive effects on gut health.
4. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress negatively impacts your gut bacteria. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and, by extension, support a healthy gut environment. Consider integrating stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine to improve both mental and gut health.
5. Get Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for the maintenance of a balanced gut microbiome. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, as poor sleep has been associated with dysbiosis (an imbalance in gut bacteria) and subsequent metabolic disturbances.
6. Limit Processed Foods and Sugars
Highly processed foods and excessive sugar intake can promote the growth of harmful bacteria in your gut. By reducing these foods in your diet, you create a more favorable environment for beneficial microorganisms.
Integrating Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Gut Health
Achieving and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is not about short-term fixes but rather a long-term commitment to a balanced lifestyle. Integrating the following habits can help you nurture your gut bacteria and, in turn, support a healthier waistline and overall well-being.
Holistic Approach to Gut Health:
- Balanced Meals: Create meals that are rich in nutrients, including a mix of proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your body’s hunger cues and avoid overeating. Mindful eating practices can prevent digestive stress and promote a balanced gut environment.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is essential for digestion and helps maintain the mucosal lining of the intestines, which is important for a healthy microbiome.
Building a Routine That Works:
Incorporating these lifestyle changes doesn’t require a complete overhaul of your daily habits. Start by making small adjustments, such as adding a serving of vegetables to every meal or taking a brisk walk after dinner. Over time, these minor changes can have a significant impact on your gut health and waist size.
Conclusion: Embrace a Healthier You Through Gut Optimization
The connection between gut bacteria and waist size underscores the importance of maintaining a balanced and diverse gut microbiome. By understanding the intricate role these microorganisms play in digestion, metabolism, and inflammation, you can make informed decisions that improve your overall health.
This comprehensive guide has provided insights into the basics of gut flora, its role in human health, and effective strategies to manage gut-related health issues. From optimizing your diet with high-fiber and fermented foods to incorporating regular exercise and stress management techniques, every small change contributes to a healthier gut and, consequently, a slimmer waist.
By integrating these evidence-based practices into your daily routine, you can take control of your health and work toward achieving long-term wellness. Remember, the journey to a healthier gut is a marathon, not a sprint. Continuous improvements in your lifestyle can lead to significant benefits over time.
For more detailed information and ongoing research on gut health, consider subscribing to newsletters from reputable organizations like Harvard Health Publishing and Mayo Clinic.
As you embark on this journey, keep in mind that each positive change is a step towards not just reducing waist size but also enhancing overall metabolic health. Explore trusted products, nutritional supplements, and expert advice to support your efforts, and stay informed with the latest developments in gut health research.
Ultimately, embracing a holistic approach to gut optimization could be the key to unlocking better health, improved energy levels, and a happier life. Your gut is not just a digestive organ—it’s a cornerstone of your overall well-being.