Mosquito bites are more than just an annoying itch on a summer day—they trigger a complex response in your body. When a mosquito lands on your skin, it injects saliva that not only helps it feed but also sets off an immune reaction in your body. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what really happens when a mosquito bites you, why those bites itch so much, and what you can do to minimize their occurrence. This article provides both scientific insights and practical advice to help you protect your health and enjoy your outdoor time more comfortably.
Drawing on expert sources such as the CDC, Mayo Clinic, and Healthline, we’ll dive into the fascinating interaction between mosquito saliva and your body. Whether you’re looking for effective remedies or are just curious about the science behind the itch, read on to learn everything you need to know about mosquito bites.
How Mosquito Saliva Eases Pain and Facilitates Blood Feeding

When a mosquito bites, it does more than simply pierce your skin. Its saliva contains a cocktail of enzymes and proteins that play critical roles in its feeding process. One might wonder: why do mosquitoes spit on your skin?
The Role of Saliva in Pain Relief and Blood Extraction
Mosquito saliva serves several functions. Primarily, it acts as an anticoagulant, preventing your blood from clotting so that the mosquito can feed continuously. It also contains mild anesthetic properties that help minimize the pain at the bite site. This dual action not only makes the bite less noticeable at first but also aids the mosquito in drawing blood more efficiently.
- Anticoagulant Action: The proteins in mosquito saliva interfere with the blood’s natural clotting process, ensuring that the feeding process is smooth and uninterrupted.
- Mild Anesthetic Effect: The slight numbing effect of the saliva allows the mosquito to remain undetected, which is crucial for its survival.
This remarkable adaptation is a perfect example of how nature fine-tunes even the smallest creatures for survival. For more detailed insights into how insect saliva works, check out the research at Healthline’s Insect Bite Guide.

Understanding the Allergic Reaction: Why Mosquito Bites Itch So Much
One of the most irritating aspects of a mosquito bite is the itch that follows. But why do these bites become so itchy? The answer lies in our immune system’s response to the foreign proteins introduced by mosquito saliva.
The Immunological Response Behind the Itch
When a mosquito injects its saliva into your skin, your body recognizes the proteins as foreign invaders. In response, your immune system releases histamines, which increase blood flow to the affected area and trigger inflammation. This process is responsible for the characteristic redness, swelling, and intense itching.
Inflammatory Response: The increased blood flow and immune cell activity result in the familiar raised, red bump that many of us know all too well.
Histamine Release: Histamines are chemicals produced by your immune system to combat perceived threats. Although essential for fighting off infections, they also cause the itch and swelling associated with mosquito bites.
Interestingly, the severity of the reaction can vary from person to person. Some individuals experience only mild irritation, while others may develop larger, more painful welts. For further reading on allergic reactions and histamines, refer to the Mayo Clinic’s Allergy Overview.
The Science of Mosquito Behavior: How Saliva Helps Them Suck Blood Easier
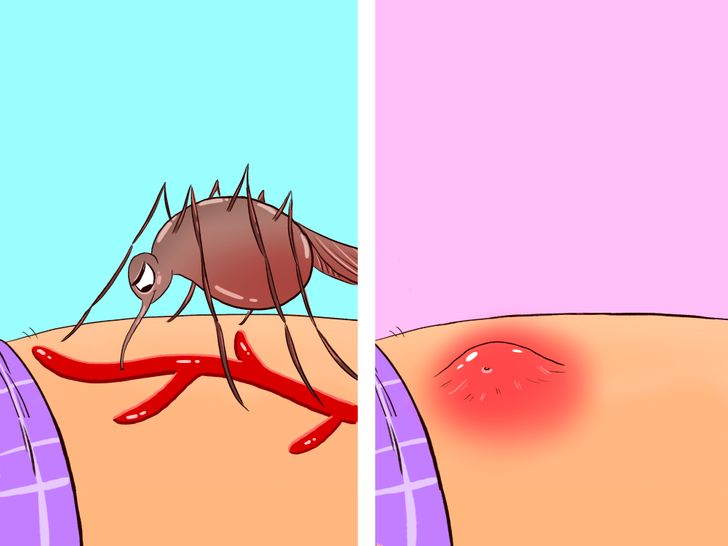
While our body reacts to the saliva, it’s important to understand how this substance benefits the mosquito. The saliva’s biochemical properties make it a vital tool in the mosquito’s feeding arsenal.
Enhancing Blood Flow with Specialized Enzymes
Mosquito saliva contains a range of enzymes that serve to break down the clotting factors in your blood. This means that as soon as the mosquito starts feeding, the blood remains in a fluid state, making it easier for the insect to extract it.
- Protein Breakdown: Certain enzymes break down fibrin, a protein crucial for blood clotting, ensuring that the blood flows freely.
- Facilitating Quick Feeding: The faster a mosquito can feed, the lower its risk of being swatted away or detected. This efficiency is key to its survival, especially in environments where predators and humans are on high alert.
Understanding these mechanisms not only highlights the ingenuity of mosquito biology but also informs the development of potential repellents or treatments that can block these enzymes. For more scientific details on how these enzymes work, you can explore articles on PubMed Central.
Effective Prevention: Top Tips and Natural Remedies to Reduce Mosquito Bites

While you can’t completely eliminate the presence of mosquitoes, there are several proven strategies and natural remedies to minimize bites and the discomfort they cause.
Practical Measures to Reduce Mosquito Exposure
- Use Insect Repellents: Choose repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or natural alternatives like lemon eucalyptus oil. These products create a barrier on your skin that deters mosquitoes.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Long sleeves, pants, and socks can help minimize exposed skin. Lightweight, breathable fabrics can keep you comfortable even on hot days.
- Install Physical Barriers: Use window screens and bed nets to keep mosquitoes out of your home, especially during peak biting hours at dawn and dusk.
- Eliminate Standing Water: Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water. Regularly check and remove water from flower pots, bird baths, and other outdoor containers.
Natural Remedies and Home Treatments
In addition to prevention, several natural remedies can help soothe mosquito bite symptoms:
- Aloe Vera: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, aloe vera gel can reduce swelling and soothe the itch.
- Tea Tree Oil: Diluted tea tree oil has antiseptic qualities that can help prevent infection if the bite is scratched.
- Baking Soda Paste: A simple mixture of baking soda and water can neutralize the pH and alleviate itching.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress or ice pack can help reduce inflammation and numb the area temporarily.
For more tips on mosquito bite prevention and treatment, visit the CDC’s Mosquito Control Page.
The Hidden Dangers: Why Preventing Mosquito Bites Matters
Beyond the immediate discomfort, mosquito bites can sometimes pose serious health risks. Mosquitoes are known carriers of diseases such as dengue fever, Zika virus, and malaria. Even in regions where these diseases are not prevalent, preventing bites is important for overall health and well-being.
Understanding Mosquito-Borne Diseases
- Disease Transmission: When mosquitoes bite, they can transfer viruses and parasites from one host to another. This is why preventing bites is not just about avoiding itchiness but also about protecting yourself from potential infections.
- Global Health Impact: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mosquito-borne illnesses are a major global health concern. Even in countries with lower risks, being proactive about bite prevention can help reduce the spread of disease.
Adopting effective mosquito control measures is crucial for public health. Regularly updating your knowledge with reliable sources, such as the CDC or WHO, can help you stay informed about current mosquito-borne disease outbreaks and prevention strategies.
Conclusion: Embracing Knowledge to Combat Mosquito Bites
Mosquito bites are a small yet significant annoyance that can have larger implications for your health. From the fascinating role of mosquito saliva in facilitating blood feeding to the immune system’s reaction that causes the infamous itch, understanding the science behind these bites can empower you to take effective preventative measures.
By using proven repellents, wearing appropriate clothing, and incorporating natural remedies into your routine, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of mosquito bites. Moreover, staying informed about the potential health risks associated with these bites underscores the importance of mosquito prevention in our daily lives.
In summary, here are the key takeaways:
- Mosquito saliva plays a crucial role in reducing pain and aiding blood extraction.
- The immune system’s allergic reaction to mosquito saliva is what causes the itch and inflammation.
- Understanding these processes can help in developing effective mosquito bite treatments and prevention strategies.
- Adopting practical measures and natural remedies can reduce your exposure to these pesky insects.
- Staying informed about mosquito-borne diseases is essential for protecting your health.
For more expert advice on insect bite treatments and prevention methods, consider checking out resources on Mayo Clinic and Healthline. By taking proactive steps and applying the insights discussed in this article, you can enjoy the outdoors with less worry and a lot more comfort.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for treatment and prevention strategies tailored to your needs.









