Melatonin, often referred to as the “sleep hormone,” has gained significant popularity as a natural sleep aid and overall health supplement. Beyond simply improving sleep quality, melatonin offers a range of benefits—from regulating circadian rhythms to boosting antioxidant defenses and supporting immune function.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll discuss 5 Reasons Why It’s Good to Take Melatonin and How to Do It. We will delve into the science behind melatonin production, examine its two primary forms, and explore the wide-ranging benefits that extend far beyond just sleep improvement. Whether you’re seeking a natural solution for sleep disorders, looking for an antioxidant boost, or interested in overall wellness, understanding how melatonin works and how to optimize its use can be a game changer.
Is It OK to Take Melatonin Every Night?
Understanding the Two Types of Melatonin in Your Body: Pineal vs. Extrapineal Melatonin
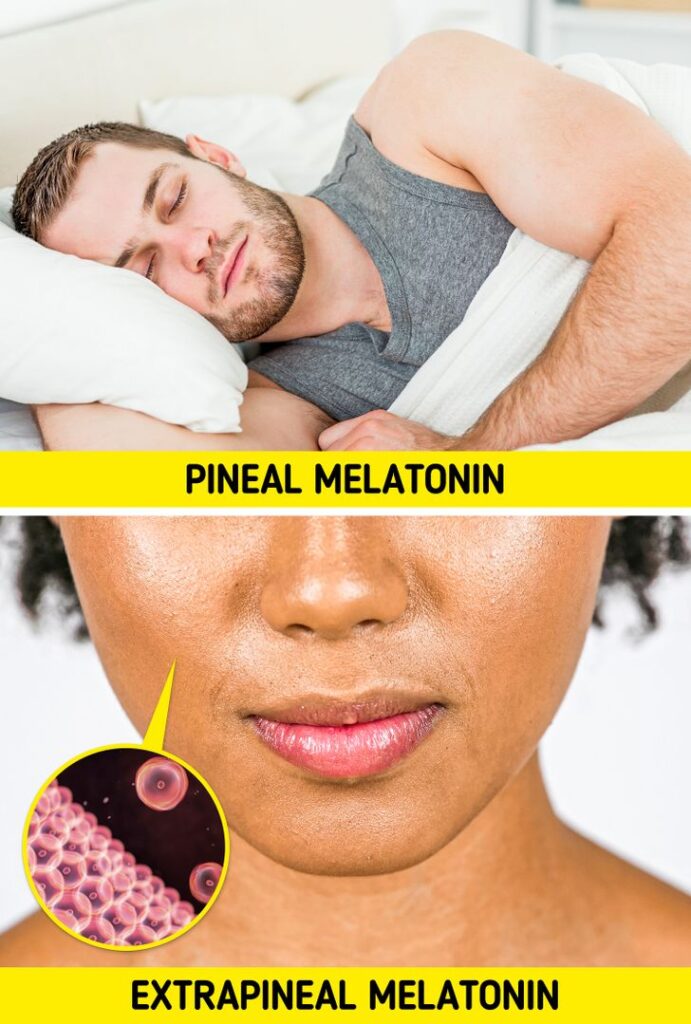
Our body produces melatonin in two primary forms: one by the pineal gland and the other by various extrapineal sources. The pineal melatonin is well-known for its role in regulating sleep cycles, while extrapineal melatonin is produced in tissues such as the retina, gastrointestinal tract, and even within the immune system. This dual production highlights the hormone’s versatility and its influence on multiple bodily functions.
The pineal gland, located in the brain, secretes melatonin in response to darkness, signaling your body that it’s time to sleep. This secretion helps maintain your circadian rhythm, ensuring that you get a consistent sleep-wake cycle. In contrast, extrapineal melatonin acts locally within tissues, where it functions as a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. This local production can protect cells from oxidative stress and support the immune response—benefits that extend beyond the realm of sleep.
Understanding these two sources is crucial for optimizing melatonin use. For instance, taking melatonin supplements may primarily impact your sleep by mimicking the natural release of the hormone from the pineal gland, while other lifestyle choices—like diet and exercise—can influence the production of extrapineal melatonin. Reputable sources such as Healthline provide further insights into how these processes work and their implications for overall health.
The Role of Pineal Melatonin in Regulating Sleep and Circadian Rhythm

One of the most well-known functions of melatonin is its ability to regulate sleep. The pineal gland’s production of melatonin is intrinsically linked to the light-dark cycle, playing a pivotal role in establishing a healthy circadian rhythm. As evening falls and darkness sets in, melatonin levels rise, preparing your body for a restful night’s sleep. Conversely, exposure to light in the morning helps suppress melatonin production, signaling that it’s time to wake up.
This natural cycle is essential for maintaining proper sleep quality and duration. Disruptions to this cycle—caused by factors such as irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen time, or exposure to artificial light—can lead to sleep disorders like insomnia. In these cases, melatonin supplements are often used as a short-term remedy to help reset the internal clock and promote better sleep.
When taken at the appropriate time—typically 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime—melatonin supplements can signal your body that it’s time to wind down. However, dosage and timing are critical factors. Too high a dose might lead to grogginess in the morning, while too low might not be effective. It’s always recommended to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen. For expert advice on dosage and timing, sources like Mayo Clinic offer trusted guidelines on how to use melatonin safely and effectively.
Extrapineal Melatonin: Its Role in Antioxidant Activity and Immune Support
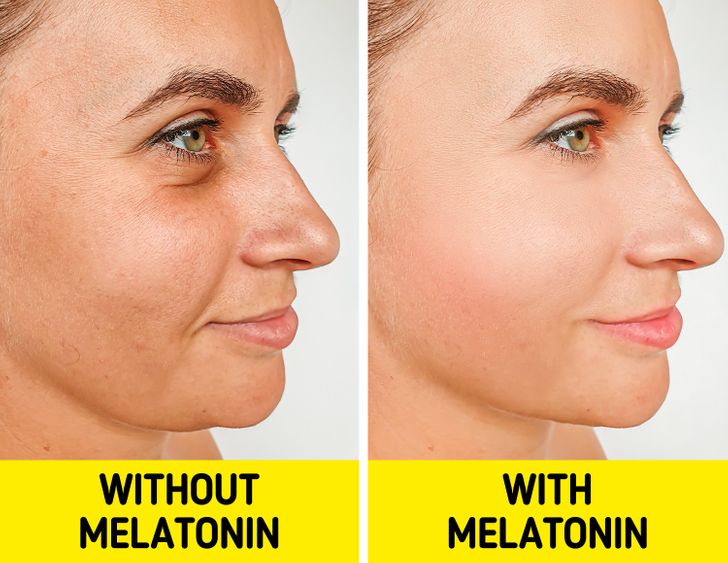
While the sleep-regulating functions of pineal melatonin are well-documented, extrapineal melatonin offers a host of other health benefits that are just as compelling. Extrapineal melatonin is produced in various tissues and is known for its strong antioxidant properties. As an antioxidant, melatonin helps neutralize free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to chronic diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular disorders.
Moreover, melatonin’s anti-inflammatory effects support immune function, helping the body fend off infections and manage inflammation. This role in immune modulation makes melatonin particularly interesting for those looking to enhance their overall health and resilience.
Research indicates that melatonin’s extrapineal production may also play a part in protecting the nervous system, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative conditions, and even supporting skin health by combating oxidative stress. For a deeper dive into the antioxidant properties of melatonin, articles from WebMD provide accessible overviews and the latest research findings.
Key Health Benefits of Melatonin: Beyond Better Sleep

Melatonin offers a wide array of benefits that extend well beyond its renowned ability to promote sleep. Here are some key health benefits that illustrate why incorporating melatonin into your routine might be a smart move:
- Improved Sleep Quality and Regulation: As previously discussed, melatonin is integral to managing sleep cycles. Better sleep not only boosts energy levels but also enhances cognitive function and mood, which are crucial for daily performance and overall well-being.
- Enhanced Immune Function: With its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, melatonin can help fortify the immune system. This is particularly beneficial during times of increased susceptibility to infections or chronic stress.
- Support for Eye Health: Extrapineal melatonin, produced in the retina, plays a role in protecting the eyes from oxidative damage and may contribute to overall eye health, an often-overlooked benefit.
- Anti-Aging and Cellular Protection: By combating free radicals, melatonin may slow the aging process at the cellular level, helping to maintain healthy skin and reducing the risk of age-related diseases.
- Neuroprotective Effects: There is growing evidence suggesting that melatonin could help protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Its antioxidant properties help preserve neuronal health, making it a topic of interest among researchers and health enthusiasts alike.
Incorporating melatonin supplements can be particularly appealing for those seeking a natural sleep aid that also offers broader health benefits. However, it’s important to use melatonin as part of a holistic approach to wellness, which includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management. For additional insights into the multifaceted benefits of melatonin, check out resources from Harvard Health Publishing.
Melatonin-Boosting Foods: Natural Ways to Enhance Your Body’s Production
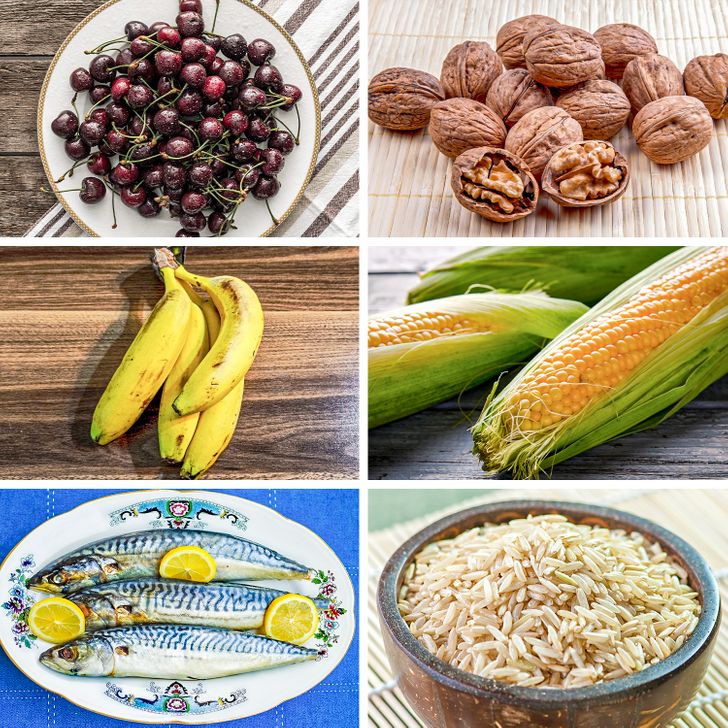

While melatonin supplements are popular, it’s also possible to boost your body’s natural production of melatonin through your diet. Certain foods are rich in melatonin or help stimulate its production, making them a valuable addition to your daily routine. Incorporating these melatonin-boosting foods can be a natural way to support your sleep quality and overall health.
Some top melatonin-rich foods include:
- Tart Cherries: Known for their high melatonin content, tart cherries and tart cherry juice have been shown to improve sleep duration and quality.
- Bananas: Rich in magnesium and potassium, bananas help relax muscles and promote a steady release of melatonin.
- Oats and Barley: These whole grains not only provide complex carbohydrates but also contain melatonin, aiding in the regulation of sleep cycles.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of melatonin as well as healthy fats and protein.
- Tomatoes and Pineapples: Both fruits are natural sources of melatonin and contribute to a balanced diet that supports sleep.
By including these foods in your meals, you can naturally enhance your body’s melatonin production without relying solely on supplements. Moreover, combining a healthy diet with other lifestyle practices—such as regular exercise and good sleep hygiene—creates a synergistic effect that can further improve your overall well-being. For detailed nutritional information and recipes that incorporate these melatonin-boosting foods, websites like EatingWell and Nutrition.gov offer valuable resources.
How to Safely Incorporate Melatonin Into Your Routine
Given the extensive benefits of melatonin, many people are curious about how to safely integrate melatonin supplements into their routine. While melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use, it’s important to follow a few key guidelines to maximize its effectiveness:
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before starting melatonin supplements, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications, seek advice from a doctor.
- Determine the Right Dosage: The ideal dosage varies based on individual factors such as age, body weight, and the specific sleep issue being addressed. Start with a low dose (typically between 0.5 to 3 mg) and adjust as necessary under professional guidance.
- Timing is Everything: For sleep-related benefits, take melatonin 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime. Avoid taking it too early or too late in the night to prevent grogginess in the morning.
- Monitor for Side Effects: While uncommon, some people may experience side effects such as headaches, dizziness, or daytime drowsiness. If you notice adverse effects, reduce the dosage or consult your healthcare provider.
- Combine with Healthy Habits: Remember that melatonin supplements work best when combined with a healthy lifestyle—regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and good sleep hygiene can significantly enhance the benefits.
By following these guidelines, you can safely incorporate melatonin into your daily routine and enjoy the multifaceted health benefits it offers.
Conclusion: Embrace the Benefits of Melatonin for Overall Well-Being
Melatonin is far more than just a sleep aid. Its roles in regulating circadian rhythms, acting as an antioxidant, and supporting immune health make it a powerful ally in your quest for better health and wellness. Whether you choose to rely on supplements or boost your natural production through diet, understanding how melatonin works and the benefits it offers can help you make informed decisions about your health.
In summary, here are the five key reasons why taking melatonin is good:
- Dual-Action Production: With distinct roles played by pineal and extrapineal melatonin, the body leverages this hormone for both sleep regulation and cellular protection.
- Sleep Optimization: Pineal melatonin helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle, making it a proven remedy for insomnia and sleep disturbances.
- Antioxidant and Immune Support: Extrapineal melatonin’s antioxidant properties protect cells from damage, while its anti-inflammatory effects support immune function.
- Broad Health Benefits: From enhancing eye health and cognitive function to providing neuroprotection and anti-aging benefits, melatonin’s advantages extend far beyond the bedroom.
- Natural Boosters: Incorporating melatonin-rich foods into your diet can help improve your body’s natural production, promoting a balanced approach to health.
As interest in natural health solutions grows, melatonin stands out as a well-researched, versatile supplement that can contribute significantly to overall well-being. Whether you’re looking to improve your sleep quality, enhance your immune system, or simply enjoy a healthier lifestyle, melatonin offers a safe and effective option when used responsibly.
For those ready to explore the benefits of melatonin further, reputable resources such as Mayo Clinic and WebMD provide expert advice and the latest research findings on this fascinating hormone. By combining these insights with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and proper sleep hygiene, you can harness the full potential of melatonin to improve your quality of life.
Embrace the power of melatonin today and take the first step towards a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. With careful usage and a holistic approach to wellness, you can enjoy the transformative benefits of melatonin and unlock a better night’s sleep, enhanced immune function, and overall vitality.
Preview photo credit TanyaLovus / Deposiphotos