Eating for optimal health isn’t just about choosing the right ingredients—it’s also about knowing which foods work best together. Modern nutritional science reveals that combining certain foods can enhance nutrient absorption, support weight loss, and even reduce inflammation. In this ultimate guide, we explore ten powerful food pairings designed to maximize health benefits. With a focus on nutrient density and flavor, these combinations are backed by research and popular dietary trends that resonate with today’s wellness enthusiasts.
Read on to uncover how pairing Salad with Olive Oil, Beef Steak with Broccoli, and other dynamic duos can transform your meal planning and elevate your overall well-being.
Food Compatibility Guide
Carotenoids And Healthy Fats
Supercharge Your Salads with Olive Oil: A Nutritional Powerhouse Pairing
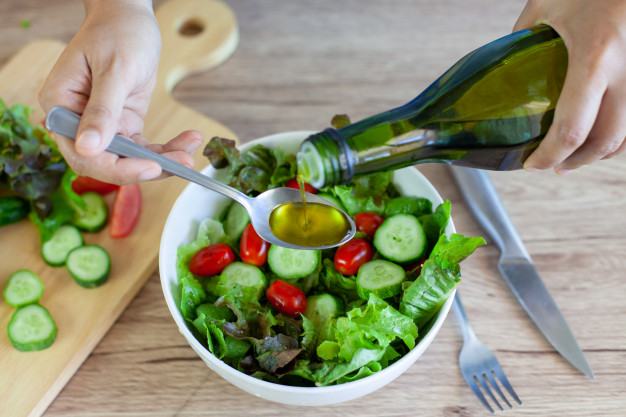

Salads are a cornerstone of healthy eating, but the secret to unlocking their full potential lies in the dressing. Extra virgin olive oil is renowned for its high levels of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, which help reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health. When combined with fresh vegetables, the healthy fats in olive oil improve the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K.
Adding olive oil not only enhances flavor but also aids in weight management and cholesterol control. Studies highlighted on Healthline suggest that diets rich in olive oil contribute to better heart health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. For a truly transformative salad experience, drizzle a tablespoon of high-quality olive oil over your greens, and consider adding a squeeze of lemon for extra zest and vitamin C.
Iron And Vitamin C
Beef Steak and Broccoli: The Protein and Antioxidant Duo for Muscle and Metabolic Health
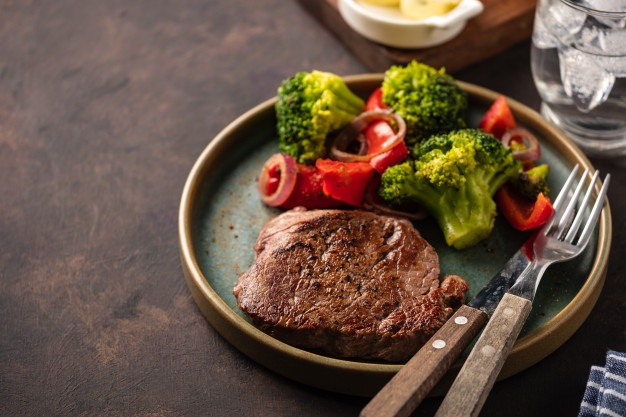

Combining beef steak with broccoli creates a synergistic meal that packs a protein punch while delivering essential antioxidants. Lean cuts of beef are an excellent source of high-quality protein and iron, crucial for muscle repair and energy production. Meanwhile, broccoli provides an array of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, along with potent antioxidants like sulforaphane that have been linked to cancer prevention and improved liver function.
This pairing is particularly beneficial for those following a low-carb or ketogenic diet, as it supports muscle growth and recovery while helping maintain a balanced metabolism. The nutrient-dense nature of beef and broccoli makes it a favorite among fitness enthusiasts and bodybuilders. For additional insights on lean protein benefits, visit Mayo Clinic.
Iron And Zinc
Wild Rice and Garlic: Boost Your Immunity with this Fiber-Rich, Flavorful Combination
Wild rice is often overshadowed by its more common counterparts, but it’s a nutritional gem. Rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential minerals, wild rice is a superb choice for maintaining steady blood sugar levels and promoting digestive health. Paired with garlic—a natural powerhouse known for its antibacterial and antiviral properties—this combination can significantly enhance your immune system.
Garlic’s active compound, allicin, not only imparts a robust flavor but also supports cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol. The marriage of wild rice and garlic creates a filling, heart-healthy meal that is perfect for those looking to optimize their overall nutrition. For more detailed nutritional advice, check out the guidelines provided by WebMD.
Vitamins B And C
Strawberries with Whole Grain Flakes: A Delicious Recipe for Antioxidant-Rich Breakfasts
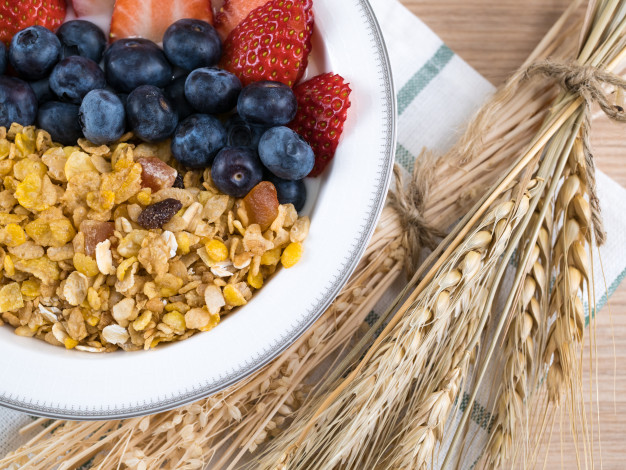

Breakfast is the most important meal of the day, and pairing strawberries with whole grain flakes is a delicious way to start. Strawberries are loaded with vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress, while whole grain flakes deliver sustained energy through complex carbohydrates and fiber. This dynamic duo not only tastes great but also supports heart health and aids in weight loss by keeping you full longer.
Incorporating strawberries into your morning routine can boost your immune system and improve skin health, thanks to their high vitamin C content. Whole grain cereals, on the other hand, have been linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. For more research-backed tips on choosing the right breakfast, refer to Harvard Health Publishing.
Iron And Vitamin C
Tofu and Bell Peppers: A Plant-Powered Pairing for Optimal Digestion and Immune Support
For vegetarians and vegans, tofu offers a versatile source of plant-based protein that pairs exceptionally well with the vibrant crunch of bell peppers. Tofu is not only rich in protein but also provides isoflavones—phytoestrogens that have been shown to have various health benefits, including lowering the risk of heart disease and certain cancers. Bell peppers, with their rich vitamin C and beta-carotene content, enhance the antioxidant profile of the meal, supporting immune function and skin health.
This pairing is particularly appealing for those looking to follow a plant-based diet without compromising on flavor or nutritional value. Combining tofu with colorful bell peppers creates a balanced meal that is both visually appealing and nutritionally complete. To explore more about the benefits of plant-based proteins, visit NutritionFacts.org.
Vitamin D And Healthy Fats
Cabbage and Salmon: A Omega-3 and Fiber-Rich Combo for Heart Health
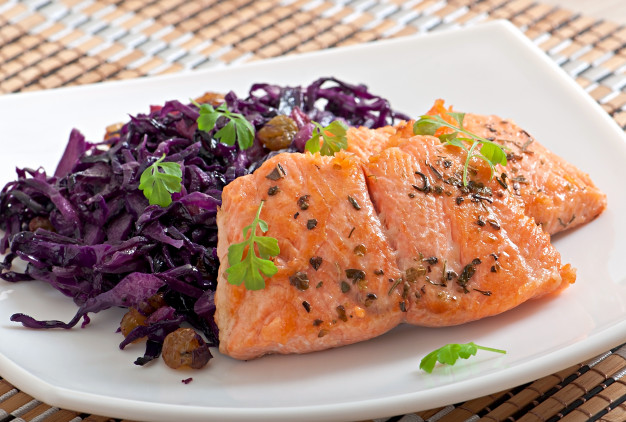

When it comes to heart health, few combinations are as powerful as cabbage and salmon. Salmon is well-known for its high omega-3 fatty acid content, which plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation, lowering blood pressure, and protecting against heart disease. Meanwhile, cabbage provides essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber that support digestive health and help manage cholesterol levels.
Together, these foods create a heart-healthy meal that not only tastes delicious but also offers profound benefits for cardiovascular wellness. This combination is ideal for individuals looking to lower their risk of heart disease while enjoying a nutrient-dense diet. For further details on the cardiovascular benefits of omega-3s, check out resources from the American Heart Association.
Carotenoids, Vitamin A, And Healthy Fats
Avocado and Tomatoes: The Ultimate Duo for Skin, Heart, and Metabolic Health
Avocado and tomatoes are a match made in nutritional heaven. Avocado is rich in healthy monounsaturated fats, which help improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. It also contains potassium and fiber, essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism. Tomatoes, on the other hand, are packed with lycopene—a powerful antioxidant linked to reduced cancer risk and improved skin health.
When combined, these ingredients create a meal that not only boosts your cardiovascular health but also promotes a glowing complexion. The creamy texture of avocado perfectly complements the tangy burst of tomatoes, making this duo a favorite in salads, salsas, and even on toast. For additional insights on the health benefits of these superfoods, visit Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Proteins And Carbohydrates
Peanut Butter and Bananas: Energy-Boosting Snacks for Optimal Brain and Body Function
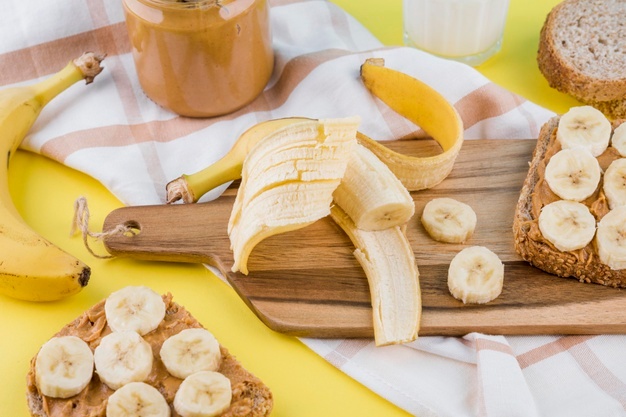

Few snacks are as universally loved as the classic pairing of peanut butter and bananas. This combination offers a balanced mix of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates, making it an ideal snack for sustained energy and improved cognitive function. Peanut butter is a rich source of vitamin E and magnesium, which support brain health, while bananas provide potassium and quick-release energy that can enhance physical performance.
This nutrient-packed snack is perfect for on-the-go breakfasts or post-workout recovery, helping to keep your energy levels stable throughout the day. Additionally, this pairing can be a delicious component of a weight loss strategy when enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. For more nutritional tips, check out articles on WebMD.
Piperine
Curry Powder and Black Pepper: Spice Up Your Meals for Enhanced Digestion and Metabolic Boost
Spices do more than just elevate the flavor of your meals—they offer significant health benefits as well. Curry powder, a blend of turmeric, cumin, coriander, and other spices, is renowned for its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to boost metabolism. When paired with black pepper, which contains piperine, the bioavailability of curcumin (the active ingredient in turmeric) is dramatically enhanced, making the anti-inflammatory effects even more potent.
This spicy duo not only helps in digestion but also supports joint health and overall immunity. Adding a pinch of curry powder and freshly ground black pepper to your dishes can transform a simple meal into a nutritional powerhouse. For a deeper dive into the benefits of spices, consider reading studies available on PubMed.
Antioxidants
Green Tea and Lemon: The Antioxidant-Rich Pairing for Detox and Immune Support
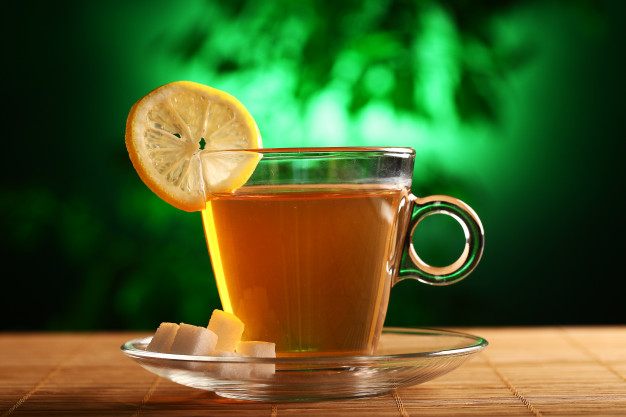

Green tea has long been celebrated for its potent antioxidants and metabolism-boosting properties. When combined with lemon, the benefits are amplified. Lemon adds a burst of vitamin C, which not only enhances the flavor of green tea but also increases the absorption of catechins—powerful antioxidants that help protect the body against free radical damage.
This refreshing combination is perfect for detoxifying your system and supporting a healthy immune function. Enjoying a cup of green tea with a slice of lemon can also improve digestion and promote clearer skin. For more insights into the health benefits of green tea, visit Harvard Health Publishing.
Conclusion: Transform Your Diet with Strategic Food Pairings
Embracing the concept of food synergy can revolutionize your approach to nutrition and wellness. By thoughtfully combining nutrient-dense foods such as Salad with Olive Oil, Beef Steak with Broccoli, Wild Rice with Garlic, and more, you can create meals that not only taste great but also provide a wide range of health benefits—from enhanced metabolism and immune support to improved heart health and weight management.
Each food pairing discussed in this guide is designed to work in harmony, unlocking hidden nutritional benefits and optimizing your overall health. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast, someone focused on weight loss, or simply looking to improve your diet, these superfood pairings can be easily incorporated into your daily meals. Use this guide as a blueprint to experiment with new combinations, refine your diet plan, and ultimately enjoy the numerous benefits of a balanced, nutrient-rich diet.
For further reading on superfoods, healthy eating, and the science behind food combinations, explore trusted resources such as NutritionFacts.org, Healthline, and American Heart Association. These external references offer comprehensive insights and research that can help guide your journey toward optimal health.
By integrating these food pairings into your lifestyle, you’re not just preparing meals—you’re crafting a holistic approach to well-being that nourishes both body and mind. Embrace the power of strategic food combinations, and take a confident step toward a healthier, more energetic you.
Based on materials from Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, NCBI, Sarah Krieger, Rosanne Rust, American Society for Nutrition (ASN)